Predictive models for IOPs measured with NCT, GAT, and ORA among patients undergoing SMILE
- PMID: 36532578
- PMCID: PMC9751611
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1030458
Predictive models for IOPs measured with NCT, GAT, and ORA among patients undergoing SMILE
Abstract
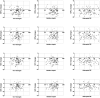
Purpose: To develop predictive models for the intraocular pressure (IOP) of patients undergoing small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE) procedures, measured with a noncontact tonometer (NCT), Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT), and an ocular response analyzer (ORA). Methods: In this prospective study, a total of 104 eyes (-6.23 ± 2.06 diopters) of 52 patients (24.38 ± 4.76 years) undergoing SMILE procedures were included. The intraocular pressure was measured (IOPNCT with NCT, IOPGAT with GAT, and IOPcc and IOPg with ORA) before surgery and at postoperative 6 months. Information on age, preoperative and attempted spherical equivalent (SE), ablation depth, preoperative values and postoperative changes in central corneal thickness (CCT), K1, K2, Km, corneal hysteresis (CH) and corneal resistance factor (CRF) values was collected in order to predict IOPs. Results: All surgeries were uneventful. At postoperative 6 months, the efficacy and safety index were 1.04 ± 0.15 and 1.08 ± 0.18, respectively. Significant decreases were detected in postoperative IOPNCT, IOPGAT, IOPcc, and IOPg compared to preoperative values (all p < 0.001). No relationship was found between any IOP and ablation depth, attempted SE, and preoperative SE, as well as CCTdifference (all p > 0.05). Predictive models for IOPs were constructed to predict preoperative values, and R 2 values were 67.5% (IOPNCT), 64.5% (IOPGAT), 78.7% (IOPcc), and 82.0% (IOPg). The prediction band of IOPNCT and IOPGAT was 7.4-15.1 mmHg and 8-16 mmHg, respectively. Conclusion: Predictive models for IOP measurements after SMILE procedures can be helpful in clinical practice.
Keywords: Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT); intraocular pressure (IOP); noncontact tonometer (NCT); ocular response analyzer (ORA); small incision lenticule extraction (SMILE).
Copyright © 2022 Han, Shi, Chen, Shen, Xu and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen K. J., Joda A., Vinciguerra R., Eliasy A., Sefat S. M. M., Kook D., et al. (2018). Clinical evaluation of a new correction algorithm for dynamic Scheimpflug analyzer tonometry before and after laser in situ keratomileusis and small-incision lenticule extraction. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 44 (5), 581–588. 10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.01.023 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen S., Lopes B. T., Huang W., Zheng X., Wang J., Zhu R., et al. (2020). Effectiveness of 4 tonometers in measuring IOP after femtosecond laser-assisted LASIK, SMILE, and transepithelial photorefractive keratectomy. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 46 (7), 967–974. 10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000000204 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

