Operationalizing and automating Data Governance
- PMID: 36532842
- PMCID: PMC9736715
- DOI: 10.1186/s40537-022-00673-5
Operationalizing and automating Data Governance
Abstract
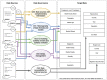
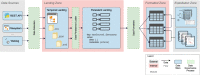
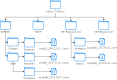
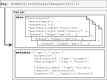
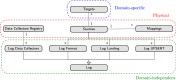
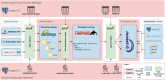
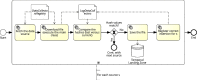
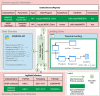
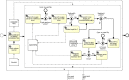
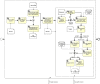
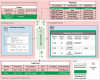
The ability to cross data from multiple sources represents a competitive advantage for organizations. Yet, the governance of the data lifecycle, from the data sources into valuable insights, is largely performed in an ad-hoc or manual manner. This is specifically concerning in scenarios where tens or hundreds of continuously evolving data sources produce semi-structured data. To overcome this challenge, we develop a framework for operationalizing and automating data governance. For the first, we propose a zoned data lake architecture and a set of data governance processes that allow the systematic ingestion, transformation and integration of data from heterogeneous sources, in order to make them readily available for business users. For the second, we propose a set of metadata artifacts that allow the automatic execution of data governance processes, addressing a wide range of data management challenges. We showcase the usefulness of the proposed approach using a real world use case, stemming from the collaborative project with the World Health Organization for the management and analysis of data about Neglected Tropical Diseases. Overall, this work contributes on facilitating organizations the adoption of data-driven strategies into a cohesive framework operationalizing and automating data governance.
Keywords: Big Data; Data Governance; Data Integration; Metadata.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Big Data Health Care Platform With Multisource Heterogeneous Data Integration and Massive High-Dimensional Data Governance for Large Hospitals: Design, Development, and Application.JMIR Med Inform. 2022 Apr 13;10(4):e36481. doi: 10.2196/36481. JMIR Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 35416792 Free PMC article.
-
Collaborative Governance for Integrated Care: Insights from a Policy Stakeholder Dialogue.Int J Integr Care. 2020 Feb 11;20(1):3. doi: 10.5334/ijic.4684. Int J Integr Care. 2020. PMID: 32089655 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Guidance for the governance of public-private collaborations in vaccine post-marketing settings in Europe.Vaccine. 2019 May 31;37(25):3278-3289. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.04.073. Epub 2019 May 6. Vaccine. 2019. PMID: 31072735 Review.
-
Socio-ecological dynamics and challenges to the governance of Neglected Tropical Disease control.Infect Dis Poverty. 2017 Feb 6;6(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40249-016-0235-5. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017. PMID: 28166826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Horrocks I, Giese M, Kharlamov E, Waaler A. Using semantic technology to tame the data variety challenge. IEEE Internet Comput. 2016;20(6):62–66. doi: 10.1109/MIC.2016.121. - DOI
-
- Popovic A, Hackney R, Tassabehji R, Castelli M. The impact of big data analytics on firms’ high value business performance. Inf Syst Front. 2018;20(2):209–222. doi: 10.1007/s10796-016-9720-4. - DOI
-
- Weill P, Ross JW. IT Governance: How Top Performers Manage IT Decision Rights for Superior Results. New York: Harvard Business Press; 2004.
-
- Khatri V, Brown CV. Designing data governance. Commun ACM. 2010;53(1):148–152. doi: 10.1145/1629175.1629210. - DOI
-
- García S, Romero O, Raventós R. DSS from an RE perspective: a systematic mapping. J Syst Softw. 2016;117:488–507. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2016.03.046. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
