Childhood emotional abuse and cyberbullying perpetration among Chinese university students: The chain mediating effects of self-esteem and problematic social media use
- PMID: 36533046
- PMCID: PMC9751917
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1036128
Childhood emotional abuse and cyberbullying perpetration among Chinese university students: The chain mediating effects of self-esteem and problematic social media use
Abstract
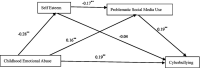
Childhood abuse has been shown to have a range of adverse physical and psychological consequences, including aggression and bullying. While researchers have explored the relationship between childhood abuse and cyberbullying, little is known about the impact of emotional abuse on cyberbullying. This study examined the link between childhood emotional abuse (CEA) and cyberbullying perpetration among university students in the Chinese cultural context, as well as the chain mediating effect of self-esteem and Problematic Social Media Use (PSMU). A total of 835 university students (18-25 years old; 293 males, 542 females; M age = 19.44 years, SD = 1.28) completed the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire Short-Form (CTQ-SF), Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale (RSES), the Social Media Use Questionnaire (SMUQ), and Cyberbullying Inventory (CBI). The results showed that CEA and PSMU were positively correlated with cyberbullying; self-esteem was negatively correlated with cyberbullying. Besides, self-esteem and PSMU sequentially mediated the relationship between CEA and cyberbullying perpetration. The findings indicate that childhood emotional abuse may lower self-esteem and cause problematic social media use, which increases cyberbullying perpetration.
Keywords: childhood emotional abuse; cyberbullying perpetration; problematic social media use; self-esteem; university students.
Copyright © 2022 Xu and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andreassen C. S., Billieux J., Griffiths M. D., Kuss D. J., Demetrovics Z., Mazzoni E., et al. . (2016). The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 30, 252–262. doi: 10.1037/adb0000160, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barlett C. P., Gentile D. A., Chng G., Li D., Chamberlin K. (2018). Social media use and cyberbullying perpetration: a longitudinal analysis. Violence Gend. 5, 191–197. doi: 10.1089/vio.2017.0047 - DOI
-
- Barlett C. P., Seyfert L. W., Simmers M. M., Chen V. H. H., Cavalcanti J. G., Krahé B., et al. . (2021). Cross-cultural similarities and differences in the theoretical predictors of cyberbullying perpetration: results from a seven-country study. Aggress. Behav. 47, 111–119. doi: 10.1002/ab.21923, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources