Exogenous ketone supplementation: an emerging tool for physiologists with potential as a metabolic therapy
- PMID: 36533967
- PMCID: PMC10103874
- DOI: 10.1113/EP090430
Exogenous ketone supplementation: an emerging tool for physiologists with potential as a metabolic therapy
Abstract
New findings: What is the topic of this review? The integrative physiological response to exogenous ketone supplementation. What advances does it highlight? The physiological effects and therapeutic potential of exogenous ketones on metabolic health, cardiovascular function, cognitive processing, and modulation of inflammatory pathways and immune function. Also highlighted are current challenges and future directions of the field.
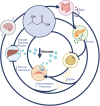
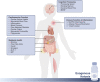
Abstract: Exogenous oral ketone supplements, primarily in form of ketone salts or esters, have emerged as a useful research tool for manipulating metabolism with potential therapeutic application targeting various aspects of several common chronic diseases. Recent literature has investigated the effects of exogenously induced ketosis on metabolic health, cardiovascular function, cognitive processing, and modulation of inflammatory pathways and immune function. This narrative review provides an overview of the integrative physiological effects of exogenous ketone supplementation and highlights current challenges and future research directions. Much of the existing research on therapeutic applications - particularly mechanistic studies - has involved pre-clinical rodent and/or cellular models, requiring further validation in human clinical studies. Existing human studies report that exogenous ketones can lower blood glucose and improve some aspects of cognitive function, highlighting the potential therapeutic application of exogenous ketones for type 2 diabetes and neurological diseases. There is also support for the ability of exogenous ketosis to improve cardiac metabolism in rodent models of heart failure with supporting human studies emerging; long-terms effects of exogenous ketone supplementation on the human cardiovascular system and lipid profiles are needed. An important avenue for future work is provided by research accelerating technologies that enable continuous ketone monitoring and/or the development of more palatable ketone mixtures that optimize plasma ketone kinetics to enable sustained ketosis. Lastly, research exploring the physiological interactions between exogenous ketones and varying metabolic states (e.g., exercise, fasting, metabolic disease) should yield important insights that can be used to maximize the health benefits of exogenous ketosis.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; cognitive function; inflammation; integrative physiology; ketone monoester; ketosis; metabolic health; metabolism; nutrition; type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 The Authors. Experimental Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
J.P.L. is volunteer Chief Scientific Officer for the Institute for Personalized Therapeutic Nutrition, a registered charity in Canada. He holds founder shares in Metabolic Insights Inc., a for‐profit company that developed non‐invasive metabolic monitoring devices.
Figures
References
-
- Aubert, G. , Martin, O. J. , Horton, J. L. , Lai, L. , Vega, R. B. , Leone, T. C. , Koves, T. , Gardell, S. J. , Krüger, M. , Hoppel, C. L. , Lewandowski, E. D. , Crawford, P. A. , Muoio, D. M. , & Kelly, D. P. (2016). The failing heart relies on ketone bodies as a fuel. Circulation, 133(8), 698–705. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baggio, L. L. , & Drucker, D. J. (2007). Biology of incretins: GLP‐1 and GIP. Gastroenterology, 132(6), 2131–2157. - PubMed
-
- Balasse, E. O. , Ooms, H. A. , & Lambilliotte, J. P. (1970). Evidence for a stimulatory effect of ketone bodies on insulin secretion in man. Hormone and Metabolic Research, 2(06), 371–372. - PubMed
-
- Bedi, K. C., Jr , Snyder, N. W. , Brandimarto, J. , Aziz, M. , Mesaros, C. , Worth, A. J. , Wang, L. L. , Javaheri, A. , Blair, I. A. , Margulies, K. B. , & Rame, J. E. (2016). Evidence for intramyocardial disruption of lipid metabolism and increased myocardial ketone utilization in advanced human heart failure. Circulation, 133(8), 706–716. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bharmal, S. H. , Cho, J. , Ramos, G. C. A. , Ko, J. , Cameron‐Smith, D. , & Petrov, M. S. (2021). Acute nutritional ketosis and its implications for plasma glucose and glucoregulatory peptides in adults with prediabetes: A crossover placebo‐controlled randomized trial. Journal of Nutrition, 151(4), 921–929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

