Dermoscopy of the Diverse Spectrum of Cutaneous Tuberculosis in the Skin of Color
- PMID: 36534549
- PMCID: PMC9681234
- DOI: 10.5826/dpc.1204a203
Dermoscopy of the Diverse Spectrum of Cutaneous Tuberculosis in the Skin of Color
Abstract
Introduction: Cutaneous tuberculosis is an uncommon form of tuberculosis, accounting for 1%-2% of all forms of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. Knowledge of the dermoscopic characteristics of different clinical types of cutaneous tuberculosis can help timely diagnosis resulting in better outcomes.
Objectives: To characterize the Dermoscopy findings in different clinical types of cutaneous tuberculosis in dark skin phototypes.
Methods: All clinically suspected and biopsy confirmed cases of cutaneous tuberculosis seen from July 2019 through December 2021 were retrospectively recruited. Information including age, gender, disease duration, site and morphology of lesions, and presence of concomitant tuberculosis elsewhere was noted. Two investigators retrospectively reviewed the dermoscopic characteristics of these cases.
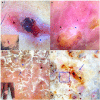
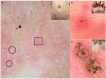
Results: Twenty-two patients comprised of 12 women and 10 men met the inclusion criteria. Lupus vulgaris was the commonest presentation of cutaneous tuberculosis seen in 13 patients. Five had scrofuloderma, 2 had tuberculosis verrucosa cutis and 1 patient each had lichen scrofulosorum and papulo-necrotic tuberculid. Yellow-orange structureless areas (100%), linear/dot vessels (100%), white scales (92.3%), and white structureless areas (84.6%) were the predominant dermoscopy findings in lupus vulgaris. In scrofuloderma, linear vessels and white structureless areas were visible in all cases. Dirty white scales with a papillated surface were characteristically seen in tuberculosis verrucosa cutis, with 1 of the 2 patients each showing vessels and yellow-orange structureless areas. White globules with surrounding erythema were seen in lichen scrofulosorum and yellow-orange structureless areas with keratin plugs in papulo-necrotic tuberculid.
Conclusions: A thorough understanding of the characteristic dermoscopy of cutaneous tuberculosis can help suspect the diagnosis early resulting in better management opportunity.
Keywords: cutaneous tuberculosis; dermoscopy; lupus vulgaris; scrofuloderma.
©2022 Jindal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
