Crizotinib in Combination With Chemotherapy for Pediatric Patients With ALK+ Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma: The Results of Children's Oncology Group Trial ANHL12P1
- PMID: 36534942
- PMCID: PMC10082271
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.22.00272
Crizotinib in Combination With Chemotherapy for Pediatric Patients With ALK+ Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma: The Results of Children's Oncology Group Trial ANHL12P1
Abstract
Purpose: Arm crizotinib (CZ) of the Children's Oncology Group trial ANHL12P1 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01979536) examined the efficacy and toxicity of adding CZ to standard chemotherapy for children with newly diagnosed, nonlocalized ALK+ CD30+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
Patients and methods: Between 2013 and 2019, 66 enrolled children received CZ with chemotherapy. Patients received a 5-day prophase followed by six chemotherapy cycles at 21-day intervals with CZ administered twice daily during each 21-day cycle. The study was temporarily closed for two periods (total 12 months) to evaluate toxicity, during which CZ was discontinued. Measurements of NPM-ALK fusion transcripts in peripheral blood were performed at diagnosis for minimal disseminated disease (MDD).
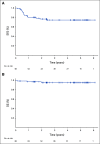
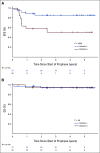
Results: The 2-year event-free survival (EFS) is 76.8% (95% CI, 68.5 to 88.1) and the 2-year overall survival is 95.2% (95% CI, 85.7 to 98.4). Fifteen patients relapsed and one patient died; median time to relapse was 7.4 months from diagnosis, with relapses occurring after chemotherapy was complete. The 66 patients completed 384 cycles of chemotherapy. Thirteen of the 66 patients experienced a grade 2+ thromboembolic adverse event (19.7%; 95% CI, 11.1 to 31.3). In the 25 patients who received mandated prophylactic anticoagulation, there were two thromboembolic events (8.0%; 95% CI, 0.01 to 26). Patients with negative MDD had a superior outcome, with an EFS of 85.6% (95% CI, 68.6 to 93.8); positive MDD was associated with a lower EFS of 58.1% (95% CI, 33.4 to 76.4).
Conclusion: Arm CZ of ANHL12P1 demonstrated that the addition of CZ to standard treatment prevented relapses during therapy for children with ALCL, MDD predicted EFS, and the addition of CZ resulted in unexpected thromboembolic events. Overall survival and EFS rates are consistent with the highest reported outcomes for children with ALCL.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
References
-
- Lowe EJ, Gross TG: Anaplastic large cell lymphoma in children and adolescents. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 30:509-519, 2013 - PubMed
-
- Sandlund JT, Downing JR, Crist WM: Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma in childhood. N Engl J Med 334:1238-1248, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Perkins SL, Pickering D, Lowe EJ, et al. : Childhood anaplastic large cell lymphoma has a high incidence of ALK gene rearrangement as determined by immunohistochemical staining and fluorescent in situ hybridisation: A genetic and pathological correlation. Br J Haematol 131:624-627, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Cleary JM, Rodig S, Barr PM, et al. : Crizotinib as salvage and maintenance with allogeneic stem cell transplantation for refractory anaplastic large cell lymphoma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 12:323-326, 2014; quiz 326 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

