Comparability of automated drusen volume measurements in age-related macular degeneration: a MACUSTAR study report
- PMID: 36535990
- PMCID: PMC9763254
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-26223-w
Comparability of automated drusen volume measurements in age-related macular degeneration: a MACUSTAR study report
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Comparability of automated drusen volume measurements in age-related macular degeneration: a MACUSTAR study report.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 7;13(1):3795. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30360-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36882430 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
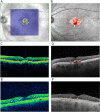
Drusen are hallmarks of early and intermediate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) but their quantification remains a challenge. We compared automated drusen volume measurements between different OCT devices. We included 380 eyes from 200 individuals with bilateral intermediate (iAMD, n = 126), early (eAMD, n = 25) or no AMD (n = 49) from the MACUSTAR study. We assessed OCT scans from Cirrus (200 × 200 macular cube, 6 × 6 mm; Zeiss Meditec, CA) and Spectralis (20° × 20°, 25 B-scans; 30° × 25°, 241 B-scans; Heidelberg Engineering, Germany) devices. Sensitivity and specificity for drusen detection and differences between modalities were assessed with intra-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) and mean difference in a 5 mm diameter fovea-centered circle. Specificity was > 90% in the three modalities. In eAMD, we observed highest sensitivity in the denser Spectralis scan (68.1). The two different Spectralis modalities showed a significantly higher agreement in quantifying drusen volume in iAMD (ICC 0.993 [0.991-0.994]) than the dense Spectralis with Cirrus scan (ICC 0.807 [0.757-0.847]). Formulae for drusen volume conversion in iAMD between the two devices are provided. Automated drusen volume measures are not interchangeable between devices and softwares and need to be interpreted with the used imaging devices and software in mind. Accounting for systematic difference between methods increases comparability and conversion formulae are provided. Less dense scans did not affect drusen volume measurements in iAMD but decreased sensitivity for medium drusen in eAMD.Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03349801. Registered on 22 November 2017.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
DG: None. JHT: Heidelberg Engineering (F), Optos (F), Zeiss (F), CenterVue (F), Novartis (R), Okko (R). OM: None. MWMW: MWMW: Heidelberg Engineering (F, R), Optos (F), Carl Zeiss Meditec (F), CenterVue (F), Heine Optotechnik GmbH (C, R, F), Berlin-Chemie AG (F), Novartis Pharma GmbH (R, F), D-Eye Srl (F), Eyenuk Inc. (F), ASKIN & CO GmbH (R), DigiSight Technologies (R). MS: Heidelberg Engineering (F), CenterVue (F), Carl Zeiss MedicTec (F). SSV: AlphaRET (C), Apellis (C, R), Bayer (F), Bioeq (C), Carl Zeiss MediTec (F), Heidelberg Engineering (F, R), Katairo (C), Kubota Vision (C), Novartis (C, F), Oxurion (C), Pixium (C), Roche (C, F), SparingVision (C), STZ GRADE Reading Center (O). MP: Apellis Pharmaceuticals (C). SHT: Heidelberg Engineering (R, F); Optos (F), Zeiss (F), CenterVue (F); Novartis (R); Bayer (R); Allergan (R). SP: Novartis (E). SL: Bayer (E). FGH: Acucela (C,F), Allergan (F), Apellis (C, F), Bayer (C, F), Boehringer-Ingelheim (C), Bioeq/Formycon (F,C), CenterVue (F), Ellex (F), Roche/Genentech (C,F), Geuder (C,F), Graybug (C), Gyroscope (C), Heidelberg Engineering (C,F), IvericBio (C, F), Kanghong (C,F), LinBioscience (C), NightStarX (F), Novartis (C,F), Optos (F), Oxurion (C), Pixium Vision (C,F), Oxurion (C), Stealth BioTherapeutics (C), Zeiss (F,C), GRADE Reading Center (O). RPF: Bayer, Santen, Ophtea, Apellis, Roche/Genentech, Böhringer-Ingelheim, Novelion, ProQR, Oxford Innovation, Roche, Alimera, Santhera, Inositec, Ellex.
Figures