Artemisitene suppresses rheumatoid arthritis progression via modulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of ICAM2 mRNA in fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- PMID: 36536495
- PMCID: PMC9763537
- DOI: 10.1002/ctm2.1148
Artemisitene suppresses rheumatoid arthritis progression via modulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of ICAM2 mRNA in fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease. We previously revealed that the natural compound artemisitene (ATT) exhibits excellent broad anticancer activities without toxicity on normal tissues. Nevertheless, the effect of ATT on RA is undiscovered. Herein, we aim to study the effect and potential mechanism of ATT on RA management.
Methods: A collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model was employed to confirm the anti-RA potential of ATT. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays, cell cycle and apoptosis analysis, immunofluorescence, migration and invasion assays, quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR), Western blot, RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis, plasmid construction and lentivirus infection, and methylated RNA immunoprecipitation and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, were carried out to confirm the effect and potential mechanism of ATT on RA management.
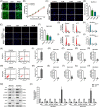
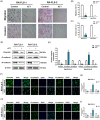
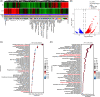
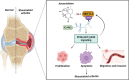
Results: ATT relieved CIA in mice. ATT inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis of RA-fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs). ATT restrained RA-FLSs migration and invasion via suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. RNA-sequencing analysis and bioinformatics analysis identified intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM2) as a promoter of RA progression in RA-FLSs. ATT inhibits RA progression by suppressing ICAM2/phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT)/p300 pathway in RA-FLSs. Moreover, ATT inhibited methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3)-mediated N6-methyladenosine methylation of ICAM2 mRNA in RA-FLSs. Interestingly, p300 directly facilitated METTL3 transcription, which could be restrained by ATT in RA-FLSs. Importantly, METTL3, ICAM2 and p300 expressions in synovium tissues of RA patients were related to clinical characteristics and therapy response.
Conclusions: We provided strong evidence that ATT has therapeutic potential for RA management by suppressing proliferation, migration and invasion, in addition to inducing apoptosis of RA-FLSs through modulating METTL3/ICAM2/PI3K/AKT/p300 feedback loop, supplying the fundamental basis for the clinical application of ATT in RA therapy. Moreover, METTL3, ICAM2 and p300 might serve as biomarkers for the therapy response of RA patients.
Keywords: ICAM2; METTL3; artemisitene; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical and Translational Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Shanghai Institute of Clinical Bioinformatics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhang S, Zhao J, Ma W. Circ‐Sirt1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and ameliorates inflammation in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast‐like synoviocytes. Autoimmunity. 2021;54(8):514‐525. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Nan H, Guo J, Liu J. NLRP12 reduces proliferation and inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast‐like synoviocytes by regulating the NF‐kappaB and MAPK pathways. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2021; 32(2):15‐22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
