Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion alters the CypA-EMMPRIN-gelatinase pathway: Implications for vascular dementia
- PMID: 36537035
- PMCID: PMC10108186
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X221146401
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion alters the CypA-EMMPRIN-gelatinase pathway: Implications for vascular dementia
Abstract
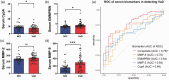
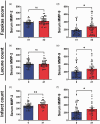
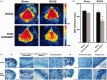
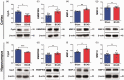
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) is postulated to underlie multiple pathophysiological processes in vascular dementia (VaD), including extracellular matrix dysfunction. While several extracellular matrix proteins, namely cyclophilin A (CypA), extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) and gelatinases (matrix metalloproteinases, MMP-2 and -9) have been investigated in acute stroke, their involvement in CCH and VaD remains unclear. In this study, CypA-EMMPRIN-gelatinase proteins were analysed in a clinical cohort of 36 aged, cognitively unimpaired subjects and 48 VaD patients, as well as in a bilateral carotid artery stenosis mouse model of CCH. Lower CypA and higher EMMPRIN levels were found in both VaD serum and CCH mouse brain. Furthermore, gelatinases were differentially altered in CCH mice and VaD patients, with significant MMP-2 increase in CCH brain and serum, whilst serum MMP-9 was elevated in VaD but reduced in CCH, suggesting complex CypA-EMMPRIN-gelatinase regulatory mechanisms. Interestingly, subjects with cortical infarcts had higher serum MMP-2, while white matter hyperintensities, cortical infarcts and lacunes were associated with higher serum MMP-9. Taken together, our data indicate that perturbations of CypA-EMMPRIN signalling may be associated with gelatinase-mediated vascular sequelae, highlighting the potential utility of the CypA-EMMPRIN-gelatinase pathway as clinical biomarkers and therapeutic targets in VaD.
Keywords: Cerebrovascular disease; chronic cerebral hypoperfusion; cyclophilin A; gelatinase; vascular dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ivabradine Induces Cardiac Protection against Myocardial Infarction by Preventing Cyclophilin-A Secretion in Pigs under Coronary Ischemia/Reperfusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 12;22(6):2902. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062902. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809359 Free PMC article.
-
EMMPRIN and its ligand cyclophilin A regulate MT1-MMP, MMP-9 and M-CSF during foam cell formation.Atherosclerosis. 2010 Mar;209(1):51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.08.029. Epub 2009 Aug 21. Atherosclerosis. 2010. PMID: 19758589
-
Cyclophilin A-EMMPRIN interaction induces invasion of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2012 Jan;27(1):198-203. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1474. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21956400
-
Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer in brain ischemia and intracerebral hemorrhage.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 31;13:986469. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.986469. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of CyPA and CD147 in cardiac remodelling.Exp Mol Pathol. 2018 Jun;104(3):222-226. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 14. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29772453 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: a critical feature in unravelling the etiology of vascular cognitive impairment.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Jun 12;11(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01590-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37309012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of ADORA3 promotes microglial phagocytosis and alleviates chronic ischemic white matter injury.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 May;30(5):e14742. doi: 10.1111/cns.14742. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38715283 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Brevican as a Biomarker of Cerebrovascular Disease in an Elderly Cognitively Impaired Cohort.Biomolecules. 2024 Jan 7;14(1):75. doi: 10.3390/biom14010075. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38254675 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics exploration of chaperone-mediated immune-proteostasis crosstalk in vascular dementia and identification of diagnostic biomarkers.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 30;16:1615540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1615540. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40808948 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Dysfunction in CNS Diseases: Paying Attention to Pericytes.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 May;31(5):e70422. doi: 10.1111/cns.70422. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 40371544 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kawamura J, Meyer JS, Terayama Y, et al.. Leukoaraiosis correlates with cerebral hypoperfusion in vascular dementia. Stroke 1991; 22: 609–614. - PubMed
-
- Obara K, Meyer JS, Muramatsu K, et al.. Lacune-associated cerebral hypoperfusion correlates with cognitive testing. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 1994; 4: 121–129. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari H, Lifschytz T, Wolf G, et al.. White matter lesions, cerebral inflammation and cognitive function in a mouse model of cerebral hypoperfusion. Brain Res 2019; 1711: 193–201. - PubMed
-
- Mracskó E, Hugyecz M, Institóris A, et al.. Changes in pro-oxidant and antioxidant enzyme levels during cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Brain Res 2010; 1321: 13–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

