Inborn errors of OAS-RNase L in SARS-CoV-2-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children
- PMID: 36538032
- PMCID: PMC10451000
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abo3627
Inborn errors of OAS-RNase L in SARS-CoV-2-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children
Abstract
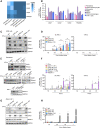
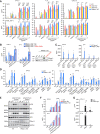
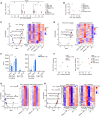
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) is a rare and severe condition that follows benign COVID-19. We report autosomal recessive deficiencies of OAS1, OAS2, or RNASEL in five unrelated children with MIS-C. The cytosolic double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-sensing OAS1 and OAS2 generate 2'-5'-linked oligoadenylates (2-5A) that activate the single-stranded RNA-degrading ribonuclease L (RNase L). Monocytic cell lines and primary myeloid cells with OAS1, OAS2, or RNase L deficiencies produce excessive amounts of inflammatory cytokines upon dsRNA or severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) stimulation. Exogenous 2-5A suppresses cytokine production in OAS1-deficient but not RNase L-deficient cells. Cytokine production in RNase L-deficient cells is impaired by MDA5 or RIG-I deficiency and abolished by mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) deficiency. Recessive OAS-RNase L deficiencies in these patients unleash the production of SARS-CoV-2-triggered, MAVS-mediated inflammatory cytokines by mononuclear phagocytes, thereby underlying MIS-C.
Figures



References
-
- Levin A. T., Hanage W. P., Owusu-Boaitey N., Cochran K. B., Walsh S. P., Meyerowitz-Katz G., Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 35, 1123–1138 (2020). 10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhaskaran K., Bacon S., Evans S. J. W., Bates C. J., Rentsch C. T., MacKenna B., Tomlinson L., Walker A. J., Schultze A., Morton C. E., Grint D., Mehrkar A., Eggo R. M., Inglesby P., Douglas I. J., McDonald H. I., Cockburn J., Williamson E. J., Evans D., Curtis H. J., Hulme W. J., Parry J., Hester F., Harper S., Spiegelhalter D., Smeeth L., Goldacre B., Factors associated with deaths due to COVID-19 versus other causes: Population-based cohort analysis of UK primary care data and linked national death registrations within the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 6, 100109 (2021). 10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williamson E. J., Walker A. J., Bhaskaran K., Bacon S., Bates C., Morton C. E., Curtis H. J., Mehrkar A., Evans D., Inglesby P., Cockburn J., McDonald H. I., MacKenna B., Tomlinson L., Douglas I. J., Rentsch C. T., Mathur R., Wong A. Y. S., Grieve R., Harrison D., Forbes H., Schultze A., Croker R., Parry J., Hester F., Harper S., Perera R., Evans S. J. W., Smeeth L., Goldacre B., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 584, 430–436 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q., Bastard P., Liu Z., Le Pen J., Moncada-Velez M., Chen J., Ogishi M., Sabli I. K. D., Hodeib S., Korol C., Rosain J., Bilguvar K., Ye J., Bolze A., Bigio B., Yang R., Arias A. A., Zhou Q., Zhang Y., Onodi F., Korniotis S., Karpf L., Philippot Q., Chbihi M., Bonnet-Madin L., Dorgham K., Smith N., Schneider W. M., Razooky B. S., Hoffmann H.-H., Michailidis E., Moens L., Han J. E., Lorenzo L., Bizien L., Meade P., Neehus A.-L., Ugurbil A. C., Corneau A., Kerner G., Zhang P., Rapaport F., Seeleuthner Y., Manry J., Masson C., Schmitt Y., Schlüter A., Le Voyer T., Khan T., Li J., Fellay J., Roussel L., Shahrooei M., Alosaimi M. F., Mansouri D., Al-Saud H., Al-Mulla F., Almourfi F., Al-Muhsen S. Z., Alsohime F., Al Turki S., Hasanato R., van de Beek D., Biondi A., Bettini L. R., D’Angio’ M., Bonfanti P., Imberti L., Sottini A., Paghera S., Quiros-Roldan E., Rossi C., Oler A. J., Tompkins M. F., Alba C., Vandernoot I., Goffard J.-C., Smits G., Migeotte I., Haerynck F., Soler-Palacin P., Martin-Nalda A., Colobran R., Morange P.-E., Keles S., Çölkesen F., Ozcelik T., Yasar K. K., Senoglu S., Karabela Ş. N., Rodríguez-Gallego C., Novelli G., Hraiech S., Tandjaoui-Lambiotte Y., Duval X., Laouénan C., Snow A. L., Dalgard C. L., Milner J. D., Vinh D. C., Mogensen T. H., Marr N., Spaan A. N., Boisson B., Boisson-Dupuis S., Bustamante J., Puel A., Ciancanelli M. J., Meyts I., Maniatis T., Soumelis V., Amara A., Nussenzweig M., García-Sastre A., Krammer F., Pujol A., Duffy D., Lifton R. P., Zhang S.-Y., Gorochov G., Béziat V., Jouanguy E., Sancho-Shimizu V., Rice C. M., Abel L., Notarangelo L. D., Cobat A., Su H. C., Casanova J.-L.; COVID-STORM Clinicians; COVID Clinicians; Imagine COVID Group; French COVID Cohort Study Group; CoV-Contact Cohort; Amsterdam UMC Covid-19 Biobank; COVID Human Genetic Effort; NIAID-USUHS/TAGC COVID Immunity Group , Inborn errors of type I IFN immunity in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 370, eabd4570 (2020). 10.1126/science.abd4570 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- R01 AI127372/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006504/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104887/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018521/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01 AI088364/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130345/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI111825/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AI001270/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG008956/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S032304/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AI091707/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001866/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI161444/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA274708/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI138938/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI160576/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

