Species dependence of A3 adenosine receptor pharmacology and function
- PMID: 36538251
- PMCID: PMC9763816
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-022-09910-1
Species dependence of A3 adenosine receptor pharmacology and function
Abstract
Efforts to fully understand pharmacological differences between G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) species homologues are generally not pursued in detail during the drug development process. To date, many GPCRs that have been successfully targeted are relatively well-conserved across species in amino acid sequence and display minimal variability of biological effects. However, the A3 adenosine receptor (AR), an exciting drug target for a multitude of diseases associated with tissue injury, ischemia, and inflammation, displays as little as 70% sequence identity among mammalian species (e.g., rodent vs. primate) commonly used in drug development. Consequently, the pharmacological properties of synthetic A3AR ligands vary widely, not only in binding affinity, selectivity, and signaling efficacy, but to the extent that some function as agonists in some species and antagonists in others. Numerous heterocyclic antagonists that have nM affinity at the human A3AR are inactive or weakly active at the rat and mouse A3ARs. Positive allosteric modulators, including the imidazo [4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine derivative LUF6000, are only active at human and some larger animal species that have been evaluated (rabbit and dog), but not rodents. A3AR agonists evoke systemic degranulation of rodent, but not human mast cells. The rat A3AR undergoes desensitization faster than the human A3AR, but the human homologue can be completely re-sensitized and recycled back to the cell surface. Thus, comprehensive pharmacological evaluation and awareness of potential A3AR species differences are critical in studies to further understand the basic biological functions of this unique AR subtype. Recombinant A3ARs from eight different species have been pharmacologically characterized thus far. In this review, we describe in detail current knowledge of species differences in genetic identity, G protein-coupling, receptor regulation, and both orthosteric and allosteric A3AR pharmacology.
Keywords: Adenosine receptor; Antagonist; G protein-coupled receptor; Nucleoside; Species differences.
© 2022. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Zhan-Guo Gao declares that there is no conflict of interest. John A. Auchampach declares that there is no conflict of interest. Kenneth A. Jacobson declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


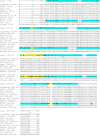
References
-
- Suratman S, Leach K, Sexton P, Felder C, Loiacono Christopoulos A. Impact of species variability and ‘probe-dependence’ on the detection and in vivo validation of allosteric modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;162:1659–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01184.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Heinz BA, Qian YW, Carter JH, Gadski RA, Beavers LS, Little SP, Yang CR, Beck JP, Hao J, Schaus JM, Svensson KA, Bruns RF. Intracellular binding site for a positive allosteric modulator of the dopamine D1 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2018;94(4):1232–1245. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.112649. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

