Therapeutic strategies for human poxvirus infections: Monkeypox (mpox), smallpox, molluscipox, and orf
- PMID: 36539022
- PMCID: PMC9758798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2022.102528
Therapeutic strategies for human poxvirus infections: Monkeypox (mpox), smallpox, molluscipox, and orf
Abstract
Therapeutic and vaccine development for human poxvirus infections (e.g., monkeypox (mpox) virus, variola virus, molluscum contagiosum virus, orf virus) has been largely deserted, especially after the eradication of smallpox by 1980. Human mpox is a self-limited disease confined to Central and West Africa for decades. However, since April 2022, mpox has quickly emerged as a multi-country outbreak, urgently calling for effective antiviral agents and vaccines to control mpox. Here, this review highlights possible therapeutic options (e.g., tecovirimat, brincidofovir, cidofovir) and other strategies (e.g., vaccines, intravenous vaccinia immune globulin) for the management of human poxvirus infections worldwide.
Keywords: Brincidofovir; Cidofovir; Monkeypox(mpox); Smallpox; Tecovirimat.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures

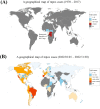
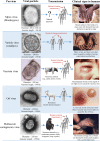

References
-
- Theves C., Crubezy E., Biagini P. History of smallpox and its spread in human populations. Microbiol Spectr. 2016;4(4) PoH-0004-2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

