Virus Detection and Identification in Minutes Using Single-Particle Imaging and Deep Learning
- PMID: 36541630
- PMCID: PMC9836350
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.2c10159
Virus Detection and Identification in Minutes Using Single-Particle Imaging and Deep Learning
Abstract
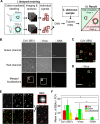
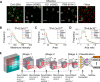
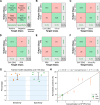
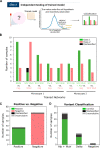
The increasing frequency and magnitude of viral outbreaks in recent decades, epitomized by the COVID-19 pandemic, has resulted in an urgent need for rapid and sensitive diagnostic methods. Here, we present a methodology for virus detection and identification that uses a convolutional neural network to distinguish between microscopy images of fluorescently labeled intact particles of different viruses. Our assay achieves labeling, imaging, and virus identification in less than 5 min and does not require any lysis, purification, or amplification steps. The trained neural network was able to differentiate SARS-CoV-2 from negative clinical samples, as well as from other common respiratory pathogens such as influenza and seasonal human coronaviruses. We were also able to differentiate closely related strains of influenza, as well as SARS-CoV-2 variants. Additional and novel pathogens can easily be incorporated into the test through software updates, offering the potential to rapidly utilize the technology in future infectious disease outbreaks or pandemics. Single-particle imaging combined with deep learning therefore offers a promising alternative to traditional viral diagnostic and genomic sequencing methods and has the potential for significant impact.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; fluorescence microscopy; influenza; machine learning; viral diagnostics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): The work was carried out using a wide-field microscope from Oxford Nanoimaging, a company in which A.N.K. is a co-founder and shareholder, and is being commercialized by Pictura Bio, a company in which N.C.R. and N.S. are co-founders. Patent applications relating to the work have been submitted by N.C.R., A.N.K., and N.S. (PCT/GB2019/053073 and PCT/GB2021/050990).
Figures

References
-
- Lamb L. E.; Bartolone S. N.; Ward E.; Chancellor M. B. Rapid detection of novel coronavirus/Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS One 2020, 15 (6), e0234682.10.1371/journal.pone.0234682. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y.; Odiwuor N.; Xiong J.; Sun L.; Nyaruaba R. O.; Wei H.; Tanner N. A. Rapid Molecular Detection of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Virus RNA Using Colorimetric LAMP. medRxiv 2020, 2020.02.26.20028373(accessed July 07, 2020)10.1101/2020.02.26.20028373. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

