Assessment of mouse VEGF neutralization by ranibizumab and aflibercept
- PMID: 36542626
- PMCID: PMC9770341
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0278951
Assessment of mouse VEGF neutralization by ranibizumab and aflibercept
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the interaction between ranibizumab, aflibercept, and mouse vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), both in vivo and in vitro.
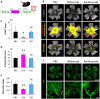
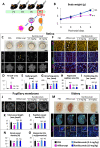
Methods: In vivo, the effect of intravitreal injection of ranibizumab and aflibercept on oxygen induced retinopathy (OIR) and the effect of multiple intraperitoneal injections of ranibizumab and aflibercept on neonatal mice were assessed. In vitro, the interaction of mouse VEGF-A with aflibercept or ranibizumab as the primary antibody was analyzed by Western blot.
Results: In both experiments using intravitreal injections in OIR mice and multiple intraperitoneal injections in neonatal mice, anti-VEGF effects were observed with aflibercept, but not with ranibizumab. Western blot analysis showed immunoreactive bands for mouse VEGF-A in the aflibercept-probed blot, but not in the ranibizumab-probed blot.
Conclusions: Aflibercept but not ranibizumab interacts with mouse VEGF, both in vivo and in vitro. When conducting experiments using anti-VEGF drugs in mice, aflibercept is suitable, but ranibizumab is not.
Copyright: © 2022 Ichiyama et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Brown DM, Kaiser PK, Michels M, Soubrane G, Heier JS, Kim RY, et al.; ANCHOR Study Group. Ranibizumab versus verteporfin for neovascular agerelated macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006. Oct 5;355(14):1432–1444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

