Must countries shoulder the burden of mesothelioma to ban asbestos? A global assessment
- PMID: 36543384
- PMCID: PMC9772623
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2022-010553
Must countries shoulder the burden of mesothelioma to ban asbestos? A global assessment
Abstract
Introduction: Mesothelioma is a key asbestos-related disease (ARD) but can be difficult to diagnose. Countries presumably ban asbestos to reduce future ARD burdens, but it is unknown if countries ban asbestos as a consequence of ARD burdens. We assessed if and to what extent mesothelioma burden has an impact on a country banning asbestos and obtaining targets for preventative strategies.
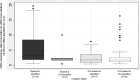
Methods: We analysed the status of asbestos ban and mesothelioma burden during 1990-2019 in 198 countries. We assessed mesothelioma burden by age-adjusted mortality rates (MRs) estimated by the Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) and mesothelioma identification by the WHO mortality database. For GBD-estimated mesothelioma MR, the pre-ban period in the asbestos-banned countries was compared with the 1990-2019 period in the not-banned countries. For mesothelioma identification, the 1990-2019 period was applied to both banned and not-banned countries.
Results: The association of mesothelioma MR with ban status increased as the ban year approached. Logistic regression analyses showed that the odds of a country banning asbestos increased 14.1-fold (95% CI 5.3 to 37.9) for mesothelioma identification combined with a 26% (12% to 42%) increase per unit increase of mesothelioma MR (one death per million per year) during the period 1-5 year before ban (model p<0.0001).
Conclusion: Mesothelioma burden had an impact on, and together with its identification, explained the banning of asbestos in many countries. Asbestos-banned countries likely learnt lessons from their historical policies of using asbestos because mesothelioma burden and identification follow historical asbestos use. Prevention targets for ARD elimination should combine asbestos ban with mesothelioma identification.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Prevention strategies; Public Health.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO/ILO joint estimates of the work-related burden of disease and injury. Available: https://www.who.int/teams/environment-climate-change-and-health/monitori... [Accessed 06 Jun 2022].
-
- Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration, Kocarnik JM, Compton K, et al. Cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life years for 29 cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. JAMA Oncol 2022;8:420–44. 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.6987 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
