Potent high-avidity neutralizing antibodies and T cell responses after COVID-19 vaccination in individuals with B cell lymphoma and multiple myeloma
- PMID: 36543907
- PMCID: PMC9886553
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-022-00502-x
Potent high-avidity neutralizing antibodies and T cell responses after COVID-19 vaccination in individuals with B cell lymphoma and multiple myeloma
Abstract
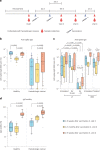
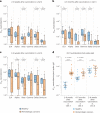
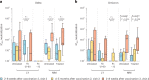
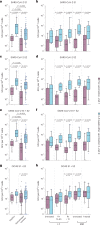
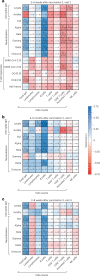
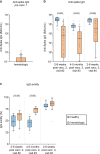
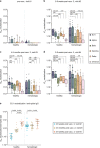
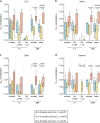
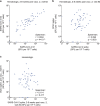
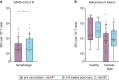
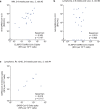
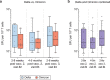
Individuals with hematologic malignancies are at increased risk for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), yet profound analyses of COVID-19 vaccine-induced immunity are scarce. Here we present an observational study with expanded methodological analysis of a longitudinal, primarily BNT162b2 mRNA-vaccinated cohort of 60 infection-naive individuals with B cell lymphomas and multiple myeloma. We show that many of these individuals, despite markedly lower anti-spike IgG titers, rapidly develop potent infection neutralization capacities against several severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 variants of concern (VoCs). The observed increased neutralization capacity per anti-spike antibody unit was paralleled by an early step increase in antibody avidity between the second and third vaccination. All individuals with hematologic malignancies, including those depleted of B cells and individuals with multiple myeloma, exhibited a robust T cell response to peptides derived from the spike protein of VoCs Delta and Omicron (BA.1). Consistently, breakthrough infections were mainly of mild to moderate severity. We conclude that COVID-19 vaccination can induce broad antiviral immunity including ultrapotent neutralizing antibodies with high avidity in different hematologic malignancies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Two approaches to tackling COVID-19 in patients with blood cancer.Nat Cancer. 2023 Jan;4(1):5-6. doi: 10.1038/s43018-022-00505-8. Nat Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36721072 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

