Guiding the choice of informatics software and tools for lipidomics research applications
- PMID: 36543939
- PMCID: PMC10263382
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-022-01710-0
Guiding the choice of informatics software and tools for lipidomics research applications
Abstract
Progress in mass spectrometry lipidomics has led to a rapid proliferation of studies across biology and biomedicine. These generate extremely large raw datasets requiring sophisticated solutions to support automated data processing. To address this, numerous software tools have been developed and tailored for specific tasks. However, for researchers, deciding which approach best suits their application relies on ad hoc testing, which is inefficient and time consuming. Here we first review the data processing pipeline, summarizing the scope of available tools. Next, to support researchers, LIPID MAPS provides an interactive online portal listing open-access tools with a graphical user interface. This guides users towards appropriate solutions within major areas in data processing, including (1) lipid-oriented databases, (2) mass spectrometry data repositories, (3) analysis of targeted lipidomics datasets, (4) lipid identification and (5) quantification from untargeted lipidomics datasets, (6) statistical analysis and visualization, and (7) data integration solutions. Detailed descriptions of functions and requirements are provided to guide customized data analysis workflows.
© 2022. Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures
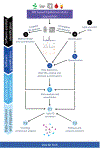


References
-
- Wenk MR The emerging field of lipidomics. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 4, 594–610 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Meikle PJ, Wong G, Barlow CK & Kingwell BA Lipidomics: Potential role in risk prediction and therapeutic monitoring for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 143, 12–23 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Yang L et al. Recent advances in lipidomics for disease research. Journal of Separation Science 39, 38–50 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

