A Novel Deep Learning Model Based on Multi-Scale and Multi-View for Detection of Pulmonary Nodules
- PMID: 36544067
- PMCID: PMC10039158
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-022-00749-x
A Novel Deep Learning Model Based on Multi-Scale and Multi-View for Detection of Pulmonary Nodules
Abstract
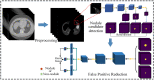
Lung cancer manifests as pulmonary nodules in the early stage. Thus, the early and accurate detection of these nodules is crucial for improving the survival rate of patients. We propose a novel two-stage model for lung nodule detection. In the candidate nodule detection stage, a deep learning model based on 3D context information roughly segments the nodules detects the preprocessed image and obtain candidate nodules. In this model, 3D image blocks are input into the constructed model, and it learns the contextual information between the various slices in the 3D image block. The parameters of our model are equivalent to those of a 2D convolutional neural network (CNN), but the model could effectively learn the 3D context information of the nodules. In the false-positive reduction stage, we propose a multi-scale shared convolutional structure model. Our lung detection model has no significant increase in parameters and computation in both stages of multi-scale and multi-view detection. The proposed model was evaluated by using 888 computed tomography (CT) scans from the LIDC-IDRI dataset and achieved a competition performance metric (CPM) score of 0.957. The average detection sensitivity per scan was 0.971/1.0 FP. Furthermore, an average detection sensitivity of 0.933/1.0 FP per scan was achieved based on data from Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital. Our model exhibited a higher detection sensitivity, a lower false-positive rate, and better generalization than current lung nodule detection methods. The method has fewer parameters and less computational complexity, which provides more possibilities for the clinical application of this method.
Keywords: 3D context information; Convolutional neural network; False-positive reduction; Lung cancer; Nodule detection.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Automatic lung nodule detection using a 3D deep convolutional neural network combined with a multi-scale prediction strategy in chest CTs.Comput Biol Med. 2018 Dec 1;103:220-231. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.10.011. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Comput Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 30390571
-
Single-view 2D CNNs with fully automatic non-nodule categorization for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Oct;165:215-224. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30337076
-
LGDNet: local feature coupling global representations network for pulmonary nodules detection.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024 Jul;62(7):1991-2004. doi: 10.1007/s11517-024-03043-w. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024. PMID: 38429443
-
An efficient multi-path 3D convolutional neural network for false-positive reduction of pulmonary nodule detection.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Dec;16(12):2269-2277. doi: 10.1007/s11548-021-02478-y. Epub 2021 Aug 27. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 34449037 Review.
-
Research progress of computer aided diagnosis system for pulmonary nodules in CT images.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(1):1-16. doi: 10.3233/XST-190581. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 31815727 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive review of pulmonary embolism imaging: past, present and future innovations in computed tomography (CT) and other diagnostic techniques.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Jun 28. doi: 10.1007/s11604-025-01811-8. Online ahead of print. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40580273 Review.
-
Multi-kernel driven 3D convolutional neural network for automated detection of lung nodules in chest CT scans.Biomed Opt Express. 2024 Jan 29;15(2):1195-1218. doi: 10.1364/BOE.504875. eCollection 2024 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2024. PMID: 38404310 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning in Thoracic Oncology: Meta-Analytical Insights into Lung Nodule Early-Detection Technologies.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Feb 12;17(4):621. doi: 10.3390/cancers17040621. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a risk screening and visualization system for pulmonary nodule in physical examination population based on feature self-recognition machine learning model.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Mar 4;11:1424750. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1424750. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40103669 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

