Last resort beta-lactam antibiotics for treatment of New-Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase producing Enterobacterales and other Difficult-to-Treat Resistance in Gram-negative bacteria: A real-life study
- PMID: 36544909
- PMCID: PMC9762507
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1048633
Last resort beta-lactam antibiotics for treatment of New-Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase producing Enterobacterales and other Difficult-to-Treat Resistance in Gram-negative bacteria: A real-life study
Abstract
Introduction: Novel last resort beta-lactam antibiotics are now available for management of infections due to New-Delhi Metallo-Beta-Lactamase (NDM) producing Enterobacterales and non-fermenters with Difficult-to-Treat Resistance. However, data regarding the use of imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam (IMI-REL), cefiderocol (CFD) and ceftazidime-avibactam plus aztreonam (CAZ-AVI-ATM) are scarce in real-life settings. This study aimed to describe the use of last resort beta-lactam antibiotics, the microbiology and the outcome, in patients hospitalized in a tertiary hospital.
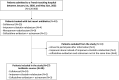
Methods: We conducted a monocentric observational cohort study from 2020/01/01, to 2022/08/31. We screened all patients admitted to Nimes University Hospital who have received ≥ 1 dose of last resort beta-lactam antibiotics during the study period, using the Pharmacy database. We included patients treated with IMI-REL, CFD and CAZ-AVI-ATM. The primary endpoint was the infection-free survival rate. We also calculated rates of microbiological and clinical cure, recurrent infection, death and adverse events.
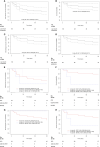
Results: Twenty-seven patients were included in the study and 30 treatment courses were analyzed: CFD (N=24; 80%), CAZ-AVI-ATM (N=3; 10%) and IMI-REL (N=3; 10%). Antibiotics were used in 21 males (70%) and 9 females (30%) with a median age at 65-year-old [50-73.5] and a median Charlson index at 1 [0-2]. Almost all the patients had ≥ 1 risk factor for carbapenem resistant bacteria, a half of them was hospitalized for severe COVID-19, and most of antibiotic courses (N=26; 87%) were associated with ICU admission. In the study population, the probability of infection-free survival at day-90 after last resort beta-lactam therapy initiation was 48.4% CI95% [33.2-70.5]. Clinical failure rate was at 30%, microbiological failure rate at 33% and mortality rate at 23%. Adverse events were documented in 5 antibiotic courses (17%). In details, P. aeruginosa were mainly treated with CFD and IMI-REL, S. maltophilia with CFD and CAZ-AVI-ATM, A. baumannii with CFD, and NDM producing-K. pneumoniae with CAZ-AVI-ATM and CFD. After a treatment course with CFD, CAZ-AVI-ATM and IMI-REL, the probability of infection-free survival was 48% CI95% [10.4-73.5], 33.3% CI95% [6.7-100], 66.7% CI95% [30-100], respectively.
Discussion/conclusion: Use of last resort beta-lactam antimicrobials in real-life settings was a safe and efficient therapeutic option for severe infections related to Gram-negative bacteria with Difficult-to-Treat Resistance.
Keywords: cefiderocol; ceftazidime-avibactam plus aztreonam; difficult to treat resistance; enterobacterales; imipenem-relebactam; metallo-beta-lactamase; new delhi metallo-beta-lactamase; pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Copyright © 2022 Larcher, Laffont-Lozes, Roger, Doncesco, Groul-Viaud, Martin, Loubet, Lavigne, Pantel and Sotto.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Balandin B., Ballesteros D., Ruiz de Luna R., López-Vergara L., Pintado V., Sancho-González M., et al. . (2021). Multicenter study of ceftolozane/tazobactam for treatment of pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in critically ill patients. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 57, 106270. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106270 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bassetti M., Echols R., Matsunaga Y., Ariyasu M., Doi Y., Ferrer R., et al. . (2020). Efficacy and safety of cefiderocol or best available therapy for the treatment of serious infections caused by carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacteria (CREDIBLE-CR): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, pathogen-focused, descriptive, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30796-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boulant T., Jousset A. B., Bonnin R. A., Barrail-Tran A., Borgel A., Oueslati S., et al. . (2019). A 2.5-year within-patient evolution of pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates with In vivo acquisition of ceftolozane-tazobactam and ceftazidime-avibactam resistance upon treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 63, e01637–e01619. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01637-19 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

