Anode optimization strategies for aqueous zinc-ion batteries
- PMID: 36545135
- PMCID: PMC9749470
- DOI: 10.1039/d2sc04945g
Anode optimization strategies for aqueous zinc-ion batteries
Abstract
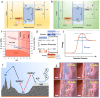
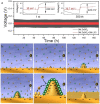
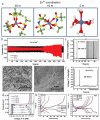
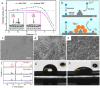
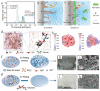
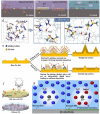
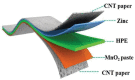
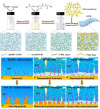
Zinc-ion batteries (ZIBs) have received much research attention due to their advantages of safety, non-toxicity, simple manufacture, and element abundance. Nevertheless, serious problems still remain for their anodes, such as dendrite development, corrosion, passivation, and the parasitic hydrogen evolution reaction due to their unique aqueous electrolyte system constituting the main issues that must be addressed, which are blocking the further advancement of anodes for Zn-ion batteries. Herein, we conduct an in-depth analysis of the problems that exist for the zinc anode, summarize the main failure types and mechanisms of the zinc anode, and review the main modification strategies for the anode from the three aspects of the electrolyte, anode surface, and anode host. Furthermore, we also shed light on further modification and optimization strategies for the zinc anode, which provide directions for the future development of anodes for zinc-ion batteries.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
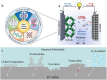
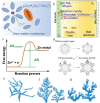
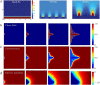
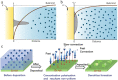


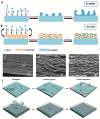
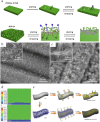
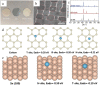
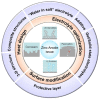
References
-
- Hannan M. A. Hoque M. M. Mohamed A. Ayob A. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2017;69:771–789. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.171. - DOI
-
- Telaretti E. Dusonchet L. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2017;75:380–392. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.003. - DOI
-
- Tong Y. Liang J. Liu H. K. Dou S. X. Energy Storage Mater. 2019;20:176–187. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2019.04.031. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

