A review on the role of miR-671 in human disorders
- PMID: 36545507
- PMCID: PMC9760869
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1077968
A review on the role of miR-671 in human disorders
Abstract
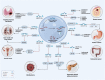
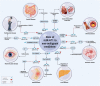
miR-671 is encoded by a gene on 7q36.1 and contributes to the pathogenesis of a variety of disorders, including diverse types of cancers, atherosclerosis, ischemic stroke, liver fibrosis, osteoarthritis, Parkinson's disease, rheumatoid arthritis, acute myocardial infarction and Crohn's disease. In the context of cancer, different studies have revealed opposite roles for this miRNA. In brief, it has been shown to be down-regulated in pancreatic ductal carcinoma, ovarian cancer, gastric cancer, osteosarcoma, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and myelodysplastic syndromes. Yet, miR-671 has been up-regulated in glioma, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in breast, lung and renal cell carcinoma have reported inconsistent results. The current review aims at summarization of the role of miR-671 in these disorders focusing on its target mRNA in each context and dysregulated signaling pathways. We also provide a summary of the role of this miRNA as a prognostic factor in malignancies.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; expression; mir-671; prognostic.
Copyright © 2022 Ghafouri-Fard, Askari, Hussen, Rasul, Hatamian, Taheri and Kiani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

