The Effect of COVID-19 Safety Protocols on Hospital Workers' Mental Health: A Moderated-Mediation Model of COVID-19 Anxiety and Psychological Resilience
- PMID: 36546960
- PMCID: PMC9774179
- DOI: 10.3390/bs12120477
The Effect of COVID-19 Safety Protocols on Hospital Workers' Mental Health: A Moderated-Mediation Model of COVID-19 Anxiety and Psychological Resilience
Abstract
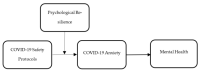
Social distancing measures can create psychological issues, especially among hospital staff who constantly deal with emergency patients. To explore the mediating role of COVID-19 anxiety on the association between COVID-19 safety protocols and mental health, and to test the moderating role of resilience between COVID-19 safety protocols and COVID-19 anxiety, this work collected data on hospital staff in terms of COVID-19 safety protocols, psychological resilience, COVID-19 anxiety, and improving staff mental health. The effects of the use of COVID-19 safety protocols on COVID-19 anxiety and the mental health of hospital workers in China were also analyzed. The experimental results showed that resilience remarkably moderated COVID-19 safety protocols and COVID-19 anxiety among Chinese hospital staff.
Keywords: COVID-19 anxiety; COVID-19 safety protocols; hospital workers; mental health; psychological resilience; stigma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of job control on hospital workers' safety performance: A moderated mediation analysis of the influences of hospital safety climate and social support.Nurs Open. 2023 Feb;10(2):781-789. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1345. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 36030533 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus anxiety, fear of COVID-19, hope and resilience in healthcare workers: a moderated mediation model study.Health Psychol Rep. 2021 Jun 28;9(4):338-397. doi: 10.5114/hpr.2021.107336. eCollection 2021. Health Psychol Rep. 2021. PMID: 38084306 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of COVID-19-Related Work Stress on the Mental Health of Primary Healthcare Workers: The Mediating Effects of Social Support and Resilience.Front Psychol. 2022 Jan 21;12:800183. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.800183. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35126252 Free PMC article.
-
The psychological impact, risk factors and coping strategies to COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare workers in the sub-Saharan Africa: a narrative review of existing literature.BMC Psychol. 2022 Dec 1;10(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s40359-022-00998-z. BMC Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36457038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of Covid-19 healthcare emergency on the psychological well-being of health professionals: a review of literature.Ann Ig. 2022 Jan-Feb;34(1):27-44. doi: 10.7416/ai.2021.2445. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Ann Ig. 2022. PMID: 33779676
References
-
- Farrell T.W., Francis L., Brown T., Ferrante L.E., Widera E., Rhodes R., Rosen T., Hwang U., Witt L.J., Thothala N., et al. Rationing Limited Healthcare Resources in the COVID-19 Era and Beyond: Ethical Considerations Regarding Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020;68:1143–1149. doi: 10.1111/jgs.16539. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gössling S., Scott D., Hall C.M. Pandemics, Tourism and Global Change: A Rapid Assessment of COVID-19. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021;29:1–20. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2020.1758708. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources