Preparation and Superstrong Adsorption of a Novel La(Ⅲ)-Crosslinked Alginate/Modified Diatomite Macroparticle Composite for Anionic Dyes Removal from Aqueous Solutions
- PMID: 36547334
- PMCID: PMC9778068
- DOI: 10.3390/gels8120810
Preparation and Superstrong Adsorption of a Novel La(Ⅲ)-Crosslinked Alginate/Modified Diatomite Macroparticle Composite for Anionic Dyes Removal from Aqueous Solutions
Abstract
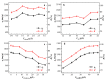
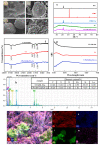
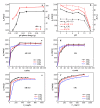
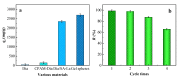
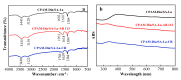
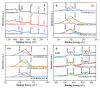
In order to solve the problem of dye pollution of the water environment, a green macroparticle composite (CPAM-Dia/SA-La) as a bioadsorbent was prepared through a sodium alginate (SA) reaction with a polyacrylamide (CPAM)-modified diatomite (Dia) and further La(III) ion crosslinking polymerization, and characterized by various analytical methods. The important preparation and adsorption conditions of the composite were explored by the adsorption of Acid blue 113 (AB 113) and Congo red (CR) dyes. The dye adsorption efficiency was evaluated. The results show that CPAM-Dia/SA-La composite prepared under the optimized conditions displays superstrong adsorption capacities of 2907 and 1578 mg/g for AB 113 and CR and almost 100% removal efficiency within 60 min adsorption time at pH 2.0 and 298 K, and they decrease slightly with the pH increase to 10. The fitting of equilibrium data to the Langmuir model is the best and the adsorption kinetic processes can be expressed by the Pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption processes are both spontaneous and exothermic. The analysis results of FT-IR and XPS revealed that the superstrong adsorption of CPAM-Dia/SA-La for dyes. The composite adsorbed by the dye can be recycled. CPAM-Dia/SA-La is a promising biosorbent for dye wastewater treatment.
Keywords: CPAM; La(III) ions; adsorption; diatomite; sodium alginate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wang Y., Wang H., Peng H., Wang Z., Wu J., Liu Z. Dye adsorption from aqueous solution by cellulose/chitosan composite: Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Fibers Polym. 2018;19:340–349. doi: 10.1007/s12221-018-7520-9. - DOI
-
- Santhanarajan A.E., Rhee C., Sul W.J., Yoo K., Seong H.J., Kim H.G., Koh S.C. Transcriptomic Analysis of Degradative Pathways for Azo Dye Acid Blue 113 in Sphingomonas melonis B-2 from the Dye Wastewater Treatment Process. Microorganisms. 2022;10:438. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10020438. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Niu P., Ha J. Efficient degradation of methyl orange via multilayer films of titanium dioxide and silicotungstic acid. Sci. ChinaChem. 2012;55:2366–2372. doi: 10.1007/s11426-012-4670-2. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 21167011/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020LH02009/Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
- XTCX003/Collaborative Innovation Center for Water Environment Security of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
- 2022JBTD009/Fundamental Research Funds for the Inner Mongolia Normal University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

