Glucose-Induced Hemodynamic and Metabolic Response of Skeletal Muscle in Heart Failure Patients with Reduced vs. Preserved Ejection Fraction-A Pilot Study
- PMID: 36547453
- PMCID: PMC9785285
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9120456
Glucose-Induced Hemodynamic and Metabolic Response of Skeletal Muscle in Heart Failure Patients with Reduced vs. Preserved Ejection Fraction-A Pilot Study
Abstract
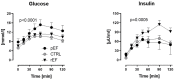
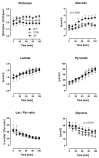
(1) Background: Insulin resistance (IR) is a characteristic pathophysiologic feature in heart failure (HF). We tested the hypothesis that skeletal muscle metabolism is differently impaired in patients with reduced (HFrEF) vs. preserved (HFpEF) ejection fraction. (2) Methods: carbohydrate and lipid metabolism was studied in situ by intramuscular microdialysis in patients with HFrEF (59 ± 14y, NYHA I-III) and HFpEF (65 ± 10y, NYHA I-II) vs. healthy subjects of similar age during the oral glucose load (oGL); (3) Results: There were no difference in fasting serum and interstitial parameters between the groups. Blood and dialysate glucose increased significantly in HFpEF vs. HFrEF and controls upon oGT (both p < 0.0001), while insulin increased significantly in HFrEF vs. HFpEF and controls (p < 0.0005). Muscle tissue perfusion tended to be lower in HFrEF vs. HFpEF and controls after the oGL (p = 0.057). There were no differences in postprandial increases in dialysate lactate and pyruvate. Postprandial dialysate glycerol was higher in HFpEF vs. HFrEF and controls upon oGL (p = 0.0016); (4) Conclusion: A pattern of muscle glucose metabolism is distinctly different in patients with HFrEF vs. HFpEF. While postprandial IR was characterized by impaired tissue perfusion and higher compensatory insulin secretion in HFrEF, reduced muscle glucose uptake and a blunted antilipolytic effect of insulin were found in HFpEF.
Keywords: insulin resistance; metabolism; microdialysis; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Son T.K., Toan N.H., Thang N., Tuong H.L.T., Tien H.A., Thuy N.H., Van Minh H., Valensi P. Prediabetes and insulin resistance in a population of patients with heart failure and reduced or preserved ejection fraction but without diabetes, overweight or hypertension. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022;21:75. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01509-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang C.D., Pan W.Q., Feng S., Quan J.W., Chen J.W., Shu X.Y., Aihemaiti M., Ding F.H., Shen W.F., Lu L., et al. Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Heart Failure with Recovered Ejection Fraction in Patients without Diabetes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022;11:e026184. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026184. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doehner W., Rauchhaus M., Ponikowski P., Godsland I.F., von Haehling S., Okonko D.O., Leyva F., Proudler A.J., Coats A.S., Anker S.D. Impaired Insulin Sensitivity as an Independent Risk Factor for Mortality in Patients with Stable Chronic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005;46:1019–1026. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.02.093. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

