Clinimetric Properties of Outcome Measures in Bronchiectasis
- PMID: 36548542
- PMCID: PMC10174126
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202206-493OC
Clinimetric Properties of Outcome Measures in Bronchiectasis
Abstract
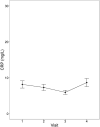
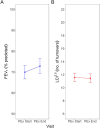
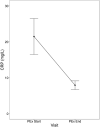
Rationale: There is a lack of outcome measures with robust clinimetric properties in bronchiectasis. Objectives: To determine the clinimetric properties (reliability over 1 year during clinical stability and responsiveness over the course of antibiotics for pulmonary exacerbation) of objective and patient-reported outcome measures. Methods: This multicenter cohort study included adults with bronchiectasis from seven hospitals in the United Kingdom. Participants attended four visits, 4 months apart over 1 year while clinically stable and at the beginning and end of exacerbation and completed lung function (spirometry and multiple breath washout), provided a blood sample for C-reactive protein (CRP) measurement, and completed health-related quality of life (HRQoL) questionnaires (Quality of Life-Bronchiectasis, St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire, and EuroQoL 5-Dimensions 5-Levels). Results: Participants (n = 132) had a mean (standard deviation) age of 66 (11) years, and 64% were female. Lung function parameters (forced expiratory volume in one second [FEV1], standard lung clearance index [LCI2.5]) were reliable over time [coefficient of variation (CV): <10%]). Regarding responsiveness, FEV1 demonstrated better properties than LCI2.5; therefore, a clear justification for the use of LCI2.5 in future trials is needed. CRP was less reliable (CV > 20%) over time than FEV1 and LCI2.5, and whereas CRP had a large mean change between the start and end of an exacerbation, this may have been driven by a small number of patients having a large change in CRP. Reliability of HRQoL questionnaires and questionnaire domains ranged from acceptable (CV: 20-30%) to good (CV: 10-20%), and HRQoL were responsive to treatment of exacerbations. Considering the specific questionnaire domain relevant to the intervention and its associated clinimetric properties is important. Additional statistics will support future power and/or sample size analysis. Conclusions: This information on the clinimetric properties of lung function parameters, CRP, and HRQoL parameters should be used to inform the choice of outcome measures used in future bronchiectasis trials.
Keywords: bronchiectasis; clinimetrics; outcome measures.
Figures



References
-
- Chalmers JD, Smith MP, McHugh BJ, Doherty C, Govan JR, Hill AT. Short- and long-term antibiotic treatment reduces airway and systemic inflammation in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2012;186:657–665. - PubMed
-
- Bilton D, Tino G, Barker AF, Chambers DC, De Soyza A, Dupont LJA, et al. B-305 Study Investigators Inhaled mannitol for non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a randomised, controlled trial. Thorax . 2014;69:1073–1079. - PubMed
-
- Haworth CS, Bilton D, Chalmers JD, Davis AM, Froehlich J, Gonda I, et al. Inhaled liposomal ciprofloxacin in patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis and chronic lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ORBIT-3 and ORBIT-4): two phase 3, randomised controlled trials. Lancet Respir Med . 2019;7:213–226. - PubMed
-
- Barker AF, O’Donnell AE, Flume P, Thompson PJ, Ruzi JD, de Gracia J, et al. Aztreonam for inhalation solution in patients with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (AIR-BX1 and AIR-BX2): two randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials. Lancet Respir Med . 2014;2:738–749. - PubMed
-
- Aksamit T, Bandel T-J, Criollo M, De Soyza A, Elborn JS, Operschall E, et al. The RESPIRE trials: two phase III, randomized, multicentre, placebo-controlled trials of ciprofloxacin dry powder for inhalation (ciprofloxacin DPI) in non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis. Contemp Clin Trials . 2017;58:78–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

