Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy in the Clinical Management of Laryngeal Dystonia
- PMID: 36548741
- PMCID: PMC9784062
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins14120844
Botulinum Neurotoxin Therapy in the Clinical Management of Laryngeal Dystonia
Abstract
Laryngeal dystonia (LD), or spasmodic dysphonia (SD), is a chronic, task-specific, focal movement disorder affecting the larynx. It interferes primarily with the essential functions of phonation and speech. LD affects patients' ability to communicate effectively and significantly diminishes their quality of life. Botulinum neurotoxin was first used as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of LD four decades ago and remains the standard of care for the treatment of LD. This article provides an overview of the clinical application of botulinum neurotoxin in the management of LD, focusing on the classification for this disorder, its pathophysiology, clinical assessment and diagnosis, the role of laryngeal electromyography and a summary of therapeutic injection techniques, including a comprehensive description of various procedural approaches, recommendations for injection sites and dosage considerations.
Keywords: botulinum neurotoxin; electromyography; injection; laryngeal dystonia; spasmodic dysphonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
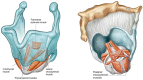



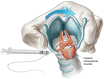
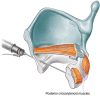

References
-
- Brin M.F., Blitzer A., Stewart C. Laryngeal dystonia (spasmodic dysphonia): Observations of 901 patients and treatment with botulinum toxin. Adv. Neurol. 1998;78:237–252. - PubMed
-
- Simonyan K., Barkmeier-Kraemer J., Blitzer A., Hallett M., Houde J.F., Jacobson Kimberley T., Ozelius L.J., Pitman M.J., Richardson R.M., Sharma N., et al. Laryngeal Dystonia. Multidiscip. Update Terminol. Pathophysiol. Res. Priorities. 2021;96:989–1001. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011922. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hyodo M., Hisa Y., Nishizawa N., Omori K., Shiromoto O., Yumoto E., Sanuki T., Nagao A., Hirose K., Kobayashi T., et al. The prevalence and clinical features of spasmodic dysphonia: A review of epidemiological surveys conducted in Japan. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021;48:179–184. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.08.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

