Direct Deaminative Functionalization
- PMID: 36548788
- PMCID: PMC10245626
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c11453
Direct Deaminative Functionalization
Abstract
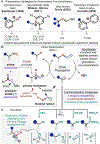
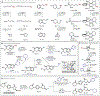
Selective functional group interconversions in complex molecular settings underpin many of the challenges facing modern organic synthesis. Currently, a privileged subset of functional groups dominates this landscape, while others, despite their abundance, are sorely underdeveloped. Amines epitomize this dichotomy; they are abundant but otherwise intransigent toward direct interconversion. Here, we report an approach that enables the direct conversion of amines to bromides, chlorides, iodides, phosphates, thioethers, and alcohols, the heart of which is a deaminative carbon-centered radical formation process using an anomeric amide reagent. Experimental and computational mechanistic studies demonstrate that successful deaminative functionalization relies not only on outcompeting the H-atom transfer to the incipient radical but also on the generation of polarity-matched, productive chain-carrying radicals that continue to react efficiently. The overall implications of this technology for interconverting amine libraries were evaluated via high-throughput parallel synthesis and applied in the development of one-pot diversification protocols.
Figures


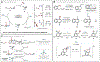
References
-
- Afagh NA; Yudin AK Chemoselectivity and the Curious Reactivity Preferences of Functional Groups. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed 2010, 49 (2), 262–310. - PubMed
-
- Schwan J; Christmann M Enabling Strategies for Step Efficient Syntheses. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47 (21), 7985–7995. - PubMed
-
- Crossley SWM; Shenvi RA A Longitudinal Study of Alkaloid Synthesis Reveals Functional Group Interconversions as Bad Actors. Chem. Rev 2015, 115 (17), 9465–9531. - PubMed
-
- Corey EJ; Cheng X-M The Logic of Chemical Synthesis, 1st ed.; Wiley: 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

