How I prevent and treat central nervous system disease in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 36548957
- PMCID: PMC10082377
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022017035
How I prevent and treat central nervous system disease in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
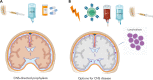
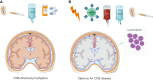
The central nervous system (CNS) is the most important site of extramedullary disease in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Although CNS disease is identified only in a minority of patients at the time of diagnosis, subsequent CNS relapses (either isolated or concurrent with other sites) occur in some patients even after the delivery of prophylactic therapy targeted to the CNS. Historically, prophylaxis against CNS disease has included intrathecal (IT) chemotherapy and radiotherapy (RT), although the latter is being used with decreasing frequency. Treatment of a CNS relapse usually involves intensive systemic therapy and cranial or craniospinal RT along with IT therapy and consideration of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. However, short- and long-term toxicities can make these interventions prohibitively risky, particularly for older adults. As new antibody-based immunotherapy agents have been approved for relapsed/refractory B-cell ALL, their use specifically for patients with CNS disease is an area of keen interest not only because of the potential for efficacy but also concerns of unique toxicity to the CNS. In this review, we discuss data-driven approaches for these common and challenging clinical scenarios as well as highlight how recent findings potentially support the use of novel immunotherapeutic strategies for CNS disease.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: R.D.C. has received research funding from Amgen, Kite/Gilead, Merck, Pfizer, Servier, and Vanda Pharmaceuticals; has reported consultancy/honoraria from Amgen, Jazz, Kite/Gilead, and Pfizer; has reported membership on the boards or advisory committees for Autolus and PeproMene Bio; and spouse-owned stock in Seagen. N.E.K. declares no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kantarjian HM, O'Brien S, Smith TL, et al. Results of treatment with hyper-CVAD, a dose-intensive regimen, in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(3):547–561. - PubMed
-
- Rowe JM, Buck G, Burnett AK, et al. Induction therapy for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of more than 1500 patients from the international ALL trial: MRC UKALL XII/ECOG E2993. Blood. 2005;106(12):3760–3767. - PubMed
-
- Huguet F, Chevret S, Leguay T, et al. Intensified therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: report of the randomized GRAALL-2005 clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(24):2514–2523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

