Metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia: mechanistic insights and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 36548959
- PMCID: PMC10375271
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022018092
Metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia: mechanistic insights and therapeutic targets
Abstract
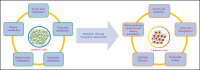
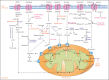
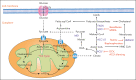
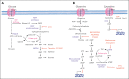
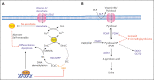
Metabolic rewiring and cellular reprogramming are trademarks of neoplastic initiation and progression in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Metabolic alteration in leukemic cells is often genotype specific, with associated changes in epigenetic and functional factors resulting in the downstream upregulation or facilitation of oncogenic pathways. Targeting abnormal or disease-sustaining metabolic activities in AML provides a wide range of therapeutic opportunities, ideally with enhanced therapeutic windows and robust clinical efficacy. This review highlights the dysregulation of amino acid, nucleotide, lipid, and carbohydrate metabolism in AML; explores the role of key vitamins and enzymes that regulate these processes; and provides an overview of metabolism-directed therapies currently in use or development.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara F, Schiffer CA. Acute myeloid leukaemia in adults. Lancet. 2013;381(9865):484–495. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, Wei AH, Appelbaum FR, et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140(12):1345–1377. - PubMed
-
- Khwaja A, Bjorkholm M, Gale RE, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2016;2(1):1–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

