Robust endoscopic image mosaicking via fusion of multimodal estimation
- PMID: 36549045
- PMCID: PMC10636739
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102709
Robust endoscopic image mosaicking via fusion of multimodal estimation
Abstract
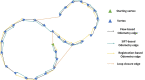
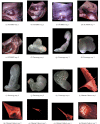
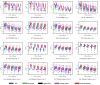
We propose an endoscopic image mosaicking algorithm that is robust to light conditioning changes, specular reflections, and feature-less scenes. These conditions are especially common in minimally invasive surgery where the light source moves with the camera to dynamically illuminate close range scenes. This makes it difficult for a single image registration method to robustly track camera motion and then generate consistent mosaics of the expanded surgical scene across different and heterogeneous environments. Instead of relying on one specialised feature extractor or image registration method, we propose to fuse different image registration algorithms according to their uncertainties, formulating the problem as affine pose graph optimisation. This allows to combine landmarks, dense intensity registration, and learning-based approaches in a single framework. To demonstrate our application we consider deep learning-based optical flow, hand-crafted features, and intensity-based registration, however, the framework is general and could take as input other sources of motion estimation, including other sensor modalities. We validate the performance of our approach on three datasets with very different characteristics to highlighting its generalisability, demonstrating the advantages of our proposed fusion framework. While each individual registration algorithm eventually fails drastically on certain surgical scenes, the fusion approach flexibly determines which algorithms to use and in which proportion to more robustly obtain consistent mosaics.
Keywords: Endoscopic image mosaicking; Image mosaicking; Medical image processing; Optical flow; Pose graph optimisation.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- Allan M., Mcleod J., Wang C.C., Rosenthal J.C., Fu K.X., Zeffiro T., Xia W., Zhanshi Z., Luo H., Zhang X., et al. 2021. Stereo correspondence and reconstruction of endoscopic data challenge. arXiv preprint arXiv:2101.01133.
-
- Bano S., Vasconcelos F., Amo M.T., Dwyer G., Gruijthuijsen C., Deprest J., Ourselin S., Vander Poorten E., Vercauteren T., Stoyanov D. Proc. Int. Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer; 2019. Deep sequential mosaicking of fetoscopic videos; pp. 311–319.
-
- Bano S., Vasconcelos F., Shepherd L.M., Vander Poorten E., Vercauteren T., Ourselin S., David A.L., Deprest J., Stoyanov D. Proc. Int. Conf. on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer; 2020. Deep placental vessel segmentation for fetoscopic mosaicking; pp. 763–773.
-
- Bartoli A. Groupwise geometric and photometric direct image registration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008;30(12):2098–2108. - PubMed

