Empagliflozin Improves the MicroRNA Signature of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Diabetes
- PMID: 36549862
- PMCID: PMC9827502
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.121.001251
Empagliflozin Improves the MicroRNA Signature of Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Diabetes
Abstract
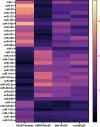
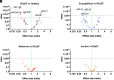
Endothelial dysfunction represents a key mechanism underlying heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), diabetes mellitus (DM), and frailty. However, reliable biomarkers to monitor endothelial dysfunction in these patients are lacking. In this study, we evaluated the expression of a panel of circulating microRNAs (miRs) involved in the regulation of endothelial function in a population of frail older adults with HFpEF and DM treated for 3 months with empagliflozin, metformin, or insulin. We identified a distinctive pattern of miRs that were significantly regulated in HFpEF patients compared to healthy controls and to HFpEF patients treated with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin. Three miRs were significantly downregulated (miR-126, miR-342-3p, and miR-638) and two were significantly upregulated (miR-21 and miR-92) in HFpEF patients compared to healthy controls. Strikingly, two of these miRs (miR-21 and miR-92) were significantly reduced in HFpEF patients after the 3-month treatment with empagliflozin, whereas no significant differences in the profile of endothelial miRs were detected in patients treated with metformin or insulin. Taken together, our findings demonstrate for the first time that specific circulating miRs involved in the regulation of endothelial function are significantly regulated in frail HFpEF patients with DM and in response to SGLT2 inhibition. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: We have identified a novel microRNA signature functionally involved in the regulation of endothelial function that is significantly regulated in frail patients with HFpEF and diabetes. Moreover, the treatment with the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin caused a modification of some of these microRNAs in a direction that was opposite to what observed in HFpEF patients, indicating a rescue of endothelial function. Our findings are relevant for clinical practice inasmuch as we were able to establish novel biomarkers of disease and response to therapy.
Copyright © 2022 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Amarasekera AT, Chang D, Schwarz P, Tan TC (2021) Does vascular endothelial dysfunction play a role in physical frailty and sarcopenia? A systematic review. Age Ageing 50:725–732. - PubMed
-
- Anker SDButler JFilippatos GFerreira JPBocchi EBöhm MBrunner-La Rocca HPChoi DJChopra VChuquiure-Valenzuela E, et al. ; EMPEROR-Preserved Trial Investigators (2021) Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 385:1451–1461. - PubMed
-
- Barwari T, Joshi A, Mayr M (2016) MicroRNAs in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 68:2577–2584. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

