High eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 expression predicts poor prognosis and may participate in the SNHG16/miR-10b-5p/EIF5A2 regulatory axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 36550070
- PMCID: PMC9833988
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24820
High eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 expression predicts poor prognosis and may participate in the SNHG16/miR-10b-5p/EIF5A2 regulatory axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: This study attempted to investigate the significance of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) in the prognosis and regulatory network of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC).
Methods: EIF5A2 expression, prognostic information, and methylation levels of HNSCC were collected from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot analyses were performed to determine EIF5A2 levels in HNSCC and normal tissue samples. R software was employed for expression analysis and prognosis assessment of EIF5A2 in HNSCC. A competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network was generated with the starBase database. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used to determine the enriched physiological functions and network related to high expression of EIF5A2 in HNSCC. Immune infiltration-related outcomes were acquired from the CIBERSORT and Tumor Immune Estimation Resource (TIMER) database.
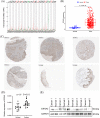
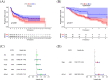
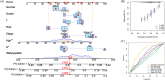
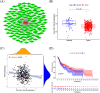
Results: EIF5A2 overexpression was observed in HNSCC and linked to poor progression-free survival and overall survival time. Cox regression analyses showed that EIF5A2 level was a stand-alone indicator of HNSCC patients' prognosis. A ceRNA network analysis highlighted the SNHG16/miR-10b-5p/EIF5A2 axis in EIF5A2 regulation. The GSEA results indicated that EIF5A2 was involved in complex signaling pathways. The CIBERSORT and TIMER databases revealed significant associations between EIF5A2 expression and immune cell infiltration.
Conclusion: EIF5A2 overexpression may be a risk factor for prognosis in HNSCC and may be regulated by the SNHG16/miR-10b-5p/EIF5A2 axis.
Keywords: The Cancer Genome Atlas; competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network; eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; prognosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-5189-3p Suppresses cell Proliferation, Invasion and Migration Through Targeting EIF5A2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biochem Genet. 2024 Jun;62(3):1603-1616. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10489-4. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37656330
-
Excavating novel diagnostic and prognostic long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: an integrated bioinformatics analysis of competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and gene co-expression networks.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12821-12838. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2003925. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34898376 Free PMC article.
-
Identification novel prognostic signatures for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma based on ceRNA network construction and immune infiltration analysis.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 19;18(5):1297-1311. doi: 10.7150/ijms.53531. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33526991 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling EIF5A2: A multifaceted player in cellular regulation, tumorigenesis and drug resistance.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 15;997:177596. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177596. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40194645 Review.
-
Prognostic significance of IL-33 and ST2 expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review.Front Oral Health. 2025 Mar 24;6:1551781. doi: 10.3389/froh.2025.1551781. eCollection 2025. Front Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40196136 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting eIF5A2 reduces invasion and reverses chemoresistance in SCC-9 cells in vitro.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Apr;39(4):463-470. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-637. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 37334930
-
Diagnostic Value of Circulating microRNAs for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of a Meta-analysis and Validation.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jan 3. doi: 10.1007/s10528-024-11001-2. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 39751721
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Auperin A. Epidemiology of head and neck cancers: an update. Curr Opin Oncol. 2020;32(3):178‐186. - PubMed
-
- Madhukar G, Subbarao N. Current and future therapeutic targets: a review on treating head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2021;21(5):386‐400. - PubMed
-
- Fang L, Gao L, Xie L, Xiao G. GC7 enhances cisplatin sensitivity via STAT3 signaling pathway inhibition and eIF5A2 inactivation in mesenchymal phenotype oral cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(3):1283‐1291. - PubMed
-
- Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, et al. Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2010;51(4):1255‐1263. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

