Downregulation of SMIM3 inhibits growth of leukemia via PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and correlates with prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype
- PMID: 36550462
- PMCID: PMC9783723
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-022-03831-8
Downregulation of SMIM3 inhibits growth of leukemia via PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and correlates with prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype
Abstract
Background: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients with normal karyotype (NK-AML) have significant variabilities in outcomes. The European Leukemia Net stratification system and some prognostic models have been used to evaluate risk stratification. However, these common standards still have some limitations. The biological functions and mechanisms of Small Integral Membrane Protein 3 (SMIM3) have seldomly been investigated. To this date, the prognostic value of SMIM3 in AML has not been reported. This study aimed to explore the clinical significance, biological effects and molecular mechanisms of SMIM3 in AML.
Methods: RT-qPCR was applied to detect the expression level of SMIM3 in bone marrow specimens from 236 newly diagnosed adult AML patients and 23 healthy volunteers. AML cell lines, Kasumi-1 and THP-1, were used for lentiviral transfection. CCK8 and colony formation assays were used to detect cell proliferation. Cell cycle and apoptosis were analyzed by flow cytometry. Western blot was performed to explore relevant signaling pathways. The biological functions of SMIM3 in vivo were validated by xenograft tumor mouse model. Survival rate was evaluated by Log-Rank test and Kaplan-Meier. Cox regression model was used to analyze multivariate analysis. The correlations between SMIM3 and drug resistance were also explored.
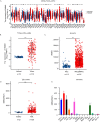
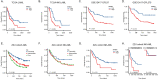
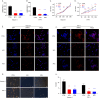
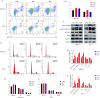
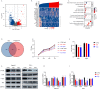
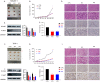
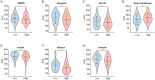
Results: Through multiple datasets and our clinical group, SMIM3 was shown to be significantly upregulated in adult AML compared to healthy subjects. SMIM3 overexpression conferred a worse prognosis and was identified as an independent prognostic factor in 95 adult NK-AML patients. Knockdown of SMIM3 inhibited cell proliferation and cell cycle progression, and induced cell apoptosis in AML cells. The reduced SMIM3 expression significantly suppressed tumor growth in the xenograft mouse model. Western blot analysis showed downregulation of p-PI3K and p-AKT in SMIM3-knockdown AML cell lines. SMIM3 may also be associated with some PI3K-AKT and first-line targeted drugs.
Conclusions: SMIM3 was highly expressed in adult AML, and such high-level expression of SMIM3 was associated with a poor prognosis in adult AML. Knockdown of SMIM3 inhibited the proliferation of AML through regulation of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. SMIM3 may serve as a potential prognostic marker and a therapeutic target for AML in the future.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Cell cycle; Cell proliferation; PI3K-AKT; Prognosis; SMIM3.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Downregulation of GNA15 Inhibits Cell Proliferation via P38 MAPK Pathway and Correlates with Prognosis of Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia With Normal Karyotype.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 6;11:724435. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.724435. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34552875 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA LINC00265 predicts the prognosis of acute myeloid leukemia patients and functions as a promoter by activating PI3K-AKT pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Nov;22(22):7867-7876. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201811_16412. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30536332
-
GRK2 Protein Mediates the ANRIL, a lncRNA, to Affect the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Kasumi-1 Cells.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Oct 21;29(10):362. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2910362. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 39473411
-
The PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathway in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 21;21(8):2907. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082907. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin module for acute myelogenous leukemia therapy: from bench to bedside.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(19):2009-23. doi: 10.2174/092986707781368423. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17691943 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioinformatic analysis and identification of macrophage polarization-related genes in intervertebral disc degeneration.Am J Transl Res. 2024 May 15;16(5):1891-1906. doi: 10.62347/HBDY5086. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38883390 Free PMC article.
-
SLC25A21 correlates with the prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia through inhibiting the growth of leukemia cells via downregulating CXCL8.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Dec 20;15(12):921. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07308-y. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39706835 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia drives shared and distinct transcriptomic changes in two invasive glioma stem cell lines.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 27;14(1):7246. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56102-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38538643 Free PMC article.
-
SMIM20: a new biological signal associated with the prognosis of glioblastoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Oct 31;12(10):2754-2763. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-796. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Transl Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37969370 Free PMC article.
-
Maresin1 alleviates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing liver macrophage pyroptosis.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 16;21(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04327-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37455316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salomé B, Gomez-Cadena A, Loyon R, Suffiotti M, Salvestrini V, Wyss T, Vanoni G, Ruan DF, Rossi M, Tozzo A, et al. CD56 as a marker of an ILC1-like population with NK cell properties that is functionally impaired in AML. Blood Adv. 2019;3:3674–3687. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018030478. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

