Clazakizumab for the treatment of chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) in kidney transplant recipients: Phase 3 IMAGINE study rationale and design
- PMID: 36550562
- PMCID: PMC9772593
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06897-3
Clazakizumab for the treatment of chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) in kidney transplant recipients: Phase 3 IMAGINE study rationale and design
Abstract
Background: Chronic active antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is a major cause of graft loss with no approved drugs for its treatment. Currently, off-label regimens are used, reflecting the high unmet need for effective therapies based on well-controlled trials. Clazakizumab is a high-affinity, humanized monoclonal antibody that binds interleukin-6 and decreases donor-specific antibody (DSA) production and inflammation. Phase 2 pilot studies of clazakizumab in kidney transplant recipients with chronic active AMR suggest modulation of DSA, stabilization of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and a manageable safety profile. We report the design of the Phase 3 IMAGINE study (NCT03744910) to evaluate the safety and efficacy of clazakizumab for the treatment of chronic active AMR.
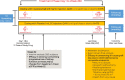
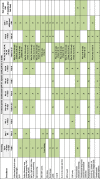
Methods: IMAGINE is a multicenter, double-blind trial of approximately 350 kidney transplant recipients with chronic active AMR (Banff chronic glomerulopathy [cg] >0 with concurrent positive human leukocyte antigen DSA) randomized 1:1 to receive clazakizumab or placebo (12.5 mg subcutaneous once every 4 weeks). The event-driven trial design will follow patients until 221 occurrences of all-cause graft loss are observed, defined as return to dialysis, graft nephrectomy, re-transplantation, estimated GFR (eGFR) <15 mL/min/1.73m2, or death from any cause. A surrogate for graft loss (eGFR slope) will be assessed at 1 year based on prior modeling validation. Secondary endpoints will include measures of pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics. Recruitment is ongoing across North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
Discussion: IMAGINE represents the first Phase 3 clinical trial investigating the safety and efficacy of clazakizumab in kidney transplant recipients with chronic active AMR, and the largest placebo-controlled trial in this patient population. This trial includes prognostic biomarker enrichment and uniquely utilizes the eGFR slope at 1 year as a surrogate endpoint for graft loss, which may accelerate the approval of a novel therapy for patients at risk of graft loss. The findings of this study will be fundamental in helping to address the unmet need for novel therapies for chronic active AMR.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03744910 . Registered on November 19, 2018.
Keywords: Chronic active antibody-mediated rejection; Clazakizumab; Estimated glomerular filtration rate; Kidney transplantation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
PWN: Consulting Fee; CSL Behring, ITB-MED. Grant/Research Support; NIH. Honoraria (Speaker); Astellas.
GAB: Consulting Fee, Grant/Research Support; Vitaeris Inc./CSL Behring.
SC: Consulting Fee; Vitaeris Inc./CSL Behring. Honoraria (Advisory Committee member); Sanofi.
RBM: Grant/Research Support; Mallinkcrodt, Transplant Genomics. Honoraria (Steering Committee member); Vitaeris.
TvG: Consulting Fee; Aurinia. Grant/Research Support; Chiesi. Honoraria (Advisory Committee member); CSL Behring. Travel; Astellas.
JCL: Ownership Interest (stock holder), Salary; CSL Behring.
SA: Ownership Interest (stock holder), Salary; CSL Behring.
EC: Salary; Vitaeris Inc./CSL Behring.
AD: Consulting Fee; CSL Behring, Care Dx. Grant/Research Support; Care Dx.
Figures
References
-
- Redfield RR, Ellis TM, Zhong W, Scalea JR, Zens TJ, Mandelbrot D, et al. Current outcomes of chronic active antibody mediated rejection - a large single center retrospective review using the updated BANFF 2013 criteria. Hum Immunol. 2016;77(4):346–352. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2016.01.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schinstock CA, Mannon RB, Budde K, Chong AS, Haas M, Knechtle S, et al. Recommended treatment for antibody-mediated rejection after kidney transplantation: The 2019 Expert Consensus From the Transplantion Society Working Group. Transplantation. 2020;104(5):911–922. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003095. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Irish W, Nickerson P, Astor BC, Chong E, Wiebe C, Moreso F, et al. Change in estimated GFR and risk of allograft failure in patients diagnosed with late active antibody-mediated rejection following kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2021;105(3):648–659. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003274. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

