Controlled Release of Encapsuled Stromal-Derived Factor 1α Improves Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Migration
- PMID: 36550960
- PMCID: PMC9774977
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9120754
Controlled Release of Encapsuled Stromal-Derived Factor 1α Improves Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Migration
Abstract
Stem cell treatment is a promising method of therapy for the group of patients whose conventional options for treatment have been limited or rejected. Stem cells have the potential to repair, replace, restore and regenerate cells. Moreover, their proliferation level is high. Owing to these features, they can be used in the treatment of numerous diseases, such as cancer, lung diseases or ischemic heart diseases. In recent years, stem cell therapy has greatly developed, shedding light on stromal-derived factor 1α (SDF-1α). SDF-1α is a mobilizing chemokine for application of endogenous stem cells to injury sites. Unfortunately, SDF-1α presented short-term results in stem cell treatment trials. Considering the tremendous benefits of this therapy, we developed biodegradable polymeric microspheres for the release of SDF-1α in a controlled and long-lasting manner. The microspheres were designed from poly(L-lactide/glycolide/trimethylene carbonate) (PLA/GA/TMC). The effect of controlled release of SDF-1α from microspheres was investigated on the migration level of bone marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (bmMSCs) derived from a pig. The study showed that SDF-1α, released from the microspheres, is more efficient at attracting bmMSCs than SDF-1α alone. This may enable the controlled delivery of selected and labeled MSCs to the destination in the future.
Keywords: SDF-1α; biodegradable polymeric microspheres; bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (bmMSCs); cell migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

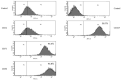

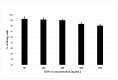

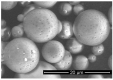

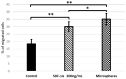
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

