Information-Based Similarity of Ordinal Pattern Sequences as a Novel Descriptor in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Screening Based on Wearable Photoplethysmography Bracelets
- PMID: 36551056
- PMCID: PMC9775447
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121089
Information-Based Similarity of Ordinal Pattern Sequences as a Novel Descriptor in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Screening Based on Wearable Photoplethysmography Bracelets
Abstract
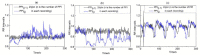
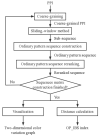
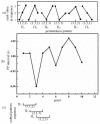
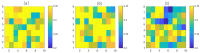
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common respiratory disorder associated with autonomic nervous system (ANS) dysfunction, resulting in abnormal heart rate variability (HRV). Capable of acquiring heart rate (HR) information with more convenience, wearable photoplethysmography (PPG) bracelets are proven to be a potential surrogate for electrocardiogram (ECG)-based devices. Meanwhile, bracelet-type PPG has been heavily marketed and widely accepted. This study aims to investigate the algorithm that can identify OSA with wearable devices. The information-based similarity of ordinal pattern sequences (OP_IBS), which is a modified version of the information-based similarity (IBS), has been proposed as a novel index to detect OSA based on wearable PPG signals. A total of 92 PPG recordings (29 normal subjects, 39 mild-moderate OSA subjects and 24 severe OSA subjects) were included in this study. OP_IBS along with classical indices were calculated. For severe OSA detection, the accuracy of OP_IBS was 85.9%, much higher than that of the low-frequency power to high-frequency power ratio (70.7%). The combination of OP_IBS, IBS, CV and LF/HF can achieve 91.3% accuracy, 91.0% sensitivity and 91.5% specificity. The performance of OP_IBS is significantly improved compared with our previous study based on the same database with the IBS method. In the Physionet database, OP_IBS also performed exceptionally well with an accuracy of 91.7%. This research shows that the OP_IBS method can access the HR dynamics of OSA subjects and help diagnose OSA in clinical environments.
Keywords: information-based similarity of ordinal pattern sequences (OP_IBS); obstructive sleep apnea (OSA); photoplethysmography (PPG); wearable bracelets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sleep apnea screening based on Photoplethysmography data from wearable bracelets using an information-based similarity approach.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Nov;211:106442. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106442. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34624633
-
Sliding Trend Fuzzy Approximate Entropy as a Novel Descriptor of Heart Rate Variability in Obstructive Sleep Apnea.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019 Jan;23(1):175-183. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2790968. Epub 2018 Jan 8. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019. PMID: 29993964
-
Validation of a photoplethysmography device for detection of obstructive sleep apnea in the perioperative setting.J Clin Monit Comput. 2019 Apr;33(2):341-345. doi: 10.1007/s10877-018-0151-2. Epub 2018 May 10. J Clin Monit Comput. 2019. PMID: 29749570
-
Can Wearable Devices Accurately Measure Heart Rate Variability? A Systematic Review.Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2018 Mar 1;60(1):7-20. doi: 10.2478/folmed-2018-0012. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2018. PMID: 29668452
-
The Accuracy of Wearable Photoplethysmography Sensors for Telehealth Monitoring: A Scoping Review.Telemed J E Health. 2023 Jun;29(6):813-828. doi: 10.1089/tmj.2022.0182. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Telemed J E Health. 2023. PMID: 36288566
Cited by
-
Detection of Sleep Apnea Using Wearable AI: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Sep 10;26:e58187. doi: 10.2196/58187. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39255014 Free PMC article.
-
Wearable Artificial Intelligence for Sleep Disorders: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2025 May 6;27:e65272. doi: 10.2196/65272. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40327852 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual-Modal Wearable Pulse Detection System Integrated with Deep Learning for High-Accuracy and Low-Power Sleep Apnea Monitoring.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jun;12(24):e2501750. doi: 10.1002/advs.202501750. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 40298874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjafield A.V., Ayas N.T., Eastwood P.R., Heinzer R., Ip M.S.M., Morrell M.J., Nunez C.M., Patel S.R., Penzel T., Pépin J.-L., et al. Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019;7:687–698. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30198-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angius G., Raffo L. A sleep apnoea keeper in a wearable device for Continuous detection and screening during daily life; Proceedings of the 2008 Computers in Cardiology; Bologna, Italy. 14–17 September 2008; pp. 433–436. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

