Picomolar or beyond Limit of Detection Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors: A Review
- PMID: 36551073
- PMCID: PMC9775238
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121107
Picomolar or beyond Limit of Detection Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors: A Review
Abstract
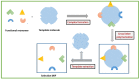
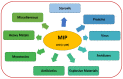
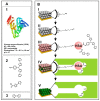
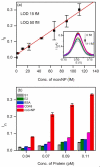
Over the last decades, molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) have emerged as selective synthetic receptors that have a selective binding site for specific analytes/target molecules. MIPs are synthetic analogues to the natural biological antigen-antibody system. Owing to the advantages they exhibit, such as high stability, simple synthetic procedure, and cost-effectiveness, MIPs have been widely used as receptors/sensors for the detection and monitoring of a variety of analytes. Moreover, integrating electrochemical sensors with MIPs offers a promising approach and demonstrates greater potential over traditional MIPs. In this review, we have compiled the methods and techniques for the production of MIP-based electrochemical sensors along with the applications of reported MIP sensors for a variety of analytes. A comprehensive in-depth analysis of recent trends reported on picomolar (pM/10-12 M)) and beyond picomolar concentration LOD (≥pM) achieved using MIPs sensors is reported. Finally, we discuss the challenges faced and put forward future perspectives along with our conclusion.
Keywords: electrochemical sensors; limit of detection; molecular imprinted polymer; ultrasensitive.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors for the Detection of Skeletal- and Cardiac-Muscle-Related Analytes.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 15;23(12):5625. doi: 10.3390/s23125625. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37420790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2024 Apr 1;249:116018. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2024.116018. Epub 2024 Jan 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2024. PMID: 38232451 Review.
-
Development of molecularly imprinted polymer based phase boundaries for sensors design (review).Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Jul;305:102693. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2022.102693. Epub 2022 May 8. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 35609398 Review.
-
Electrochemical molecularly imprinted polymer based sensors for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications (review).J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022 Jun 5;215:114739. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114739. Epub 2022 Mar 25. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022. PMID: 35429723 Review.
-
Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Combined with Electrochemical Sensors for Food Contaminants Analysis.Molecules. 2021 Jul 29;26(15):4607. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154607. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gold Nanoparticles in Nanobiotechnology: From Synthesis to Biosensing Applications.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 5;9(28):29966-29982. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10352. eCollection 2024 Jul 16. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39035946 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic In Vivo Sensing of COVID-19 Antibody Detection Using DNA-Linking Graphene Oxide Synthetic Mimic Skin Tattoo Probes.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 6;13(2):354. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020354. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005721 Free PMC article.
-
Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for the Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 26;45(1):52. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01570-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40418370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Molecularly Imprinted Fluorescence Sensor for the Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Histamine and Tyramine in Cheese.Foods. 2025 Apr 23;14(9):1475. doi: 10.3390/foods14091475. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361558 Free PMC article.
-
One-step synthesis of chiral molecularly imprinted polymer TiO2 nanoparticles for enantioseparation of phenylalanine in coated capillary electrochromatography.Mikrochim Acta. 2023 Jul 1;190(7):279. doi: 10.1007/s00604-023-05854-4. Mikrochim Acta. 2023. PMID: 37391671
References
-
- Hussain S., Zaidi S.A., Vikraman D., Kim H.-S., Jung J. Fabrication of molecularly imprinted polymer on tungsten carbide nanoparticles loaded glassy carbon as potential electrochemical sensors for oxalic acid. Microchem. J. 2020;159:105404. doi: 10.1016/j.microc.2020.105404. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

