Adaptive Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Long-Term Self-Treatment: A Review
- PMID: 36551094
- PMCID: PMC9775114
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121127
Adaptive Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Long-Term Self-Treatment: A Review
Abstract
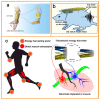
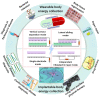
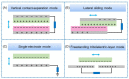
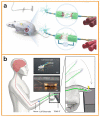
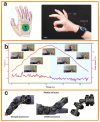
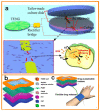
Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) were initially invented as an innovative energy-harvesting technology for scavenging mechanical energy from our bodies or the ambient environment. Through adaptive customization design, TENGs have also become a promising player in the self-powered wearable medical market for improving physical fitness and sustaining a healthy lifestyle. In addition to simultaneously harvesting our body's mechanical energy and actively detecting our physiological parameters and metabolic status, TENGs can also provide personalized medical treatment solutions in a self-powered modality. This review aims to cover the recent advances in TENG-based electronics in clinical applications, beginning from the basic working principles of TENGs and their general operation modes, continuing to the harvesting of bioenergy from the human body, and arriving at their adaptive design toward applications in chronic disease diagnosis and long-term clinical treatment. Considering the highly personalized usage scenarios, special attention is paid to customized modules that are based on TENGs and support complex medical treatments, where sustainability, biodegradability, compliance, and bio-friendliness may be critical for the operation of clinical systems. While this review provides a comprehensive understanding of TENG-based clinical devices that aims to reach a high level of technological readiness, the challenges and shortcomings of TENG-based clinical devices are also highlighted, with the expectation of providing a useful reference for the further development of such customized healthcare systems and the transfer of their technical capabilities into real-life patient care.
Keywords: adaptivity; clinical treatment; self-diagnosis; self-powered device; triboelectric nanogenerator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Chen X., Xie X., Liu Y., Zhao C., Wen M., Wen Z. Advances in Healthcare Electronics Enabled by Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:2004673. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202004673. - DOI
-
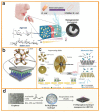
- Parandeh S., Etemadi N., Kharaziha M., Chen G., Nashalian A., Xiao X., Chen J. Advances in Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31:2105169. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202105169. - DOI
-
- Salauddin M., Rana S.S., Sharifuzzaman M., Lee S.H., Zahed M.A., Do Shin Y., Seonu S., Song H.S., Bhatta T., Park J.Y. Laser-Carbonized MXene/ZiF-67 Nanocomposite as an Intermediate Layer for Boosting the Output Performance of Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy. 2022;100:107462. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107462. - DOI
-
- Chang C.-W., Lin Y.-B., Chen J.-C. Reporting Mechanisms for Internet of Things. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2022;27:118–123. doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01713-1. - DOI
-
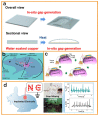
- Wang T., Li S., Tao X., Yan Q., Wang X., Chen Y., Huang F., Li H., Chen X., Bian Z. Fully Biodegradable Water-Soluble Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Human Physiological Monitoring. Nano Energy. 2022;93:106787. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106787. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

