A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality and Robot Therapy as Recent Rehabilitation Technologies Using EEG-Brain-Computer Interface Based on Movement-Related Cortical Potentials
- PMID: 36551100
- PMCID: PMC9776155
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121134
A Systematic Review of Virtual Reality and Robot Therapy as Recent Rehabilitation Technologies Using EEG-Brain-Computer Interface Based on Movement-Related Cortical Potentials
Abstract
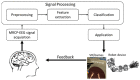
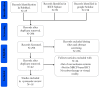
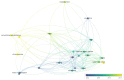
To enhance the treatment of motor function impairment, patients' brain signals for self-control as an external tool may be an extraordinarily hopeful option. For the past 10 years, researchers and clinicians in the brain-computer interface (BCI) field have been using movement-related cortical potential (MRCP) as a control signal in neurorehabilitation applications to induce plasticity by monitoring the intention of action and feedback. Here, we reviewed the research on robot therapy (RT) and virtual reality (VR)-MRCP-based BCI rehabilitation technologies as recent advancements in human healthcare. A list of 18 full-text studies suitable for qualitative review out of 322 articles published between 2000 and 2022 was identified based on inclusion and exclusion criteria. We used PRISMA guidelines for the systematic review, while the PEDro scale was used for quality evaluation. Bibliometric analysis was conducted using the VOSviewer software to identify the relationship and trends of key items. In this review, 4 studies used VR-MRCP, while 14 used RT-MRCP-based BCI neurorehabilitation approaches. The total number of subjects in all identified studies was 107, whereby 4.375 ± 6.3627 were patient subjects and 6.5455 ± 3.0855 were healthy subjects. The type of electrodes, the epoch, classifiers, and the performance information that are being used in the RT- and VR-MRCP-based BCI rehabilitation application are provided in this review. Furthermore, this review also describes the challenges facing this field, solutions, and future directions of these smart human health rehabilitation technologies. By key items relationship and trends analysis, we found that motor control, rehabilitation, and upper limb are important key items in the MRCP-based BCI field. Despite the potential of these rehabilitation technologies, there is a great scarcity of literature related to RT and VR-MRCP-based BCI. However, the information on these rehabilitation methods can be beneficial in developing RT and VR-MRCP-based BCI rehabilitation devices to induce brain plasticity and restore motor impairment. Therefore, this review will provide the basis and references of the MRCP-based BCI used in rehabilitation applications for further clinical and research development.
Keywords: biomedical signal; brain–computer interface; electroencephalography; human healthcare; machine learning; neurological diseases; robot therapy; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Use of Electroencephalography Brain-Computer Interface Systems as a Rehabilitative Approach for Upper Limb Function After a Stroke: A Systematic Review.PM R. 2017 Sep;9(9):918-932. doi: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.04.016. Epub 2017 May 13. PM R. 2017. PMID: 28512066
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of inhaler devices in asthma and chronic obstructive airways disease: a systematic review of the literature.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(26):1-149. doi: 10.3310/hta5260. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701099
-
Recommendations for the Design and Implementation of Virtual Reality for Acquired Brain Injury Rehabilitation: Systematic Review.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Jul 30;23(7):e26344. doi: 10.2196/26344. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34328434 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Robotic systems for upper-limb rehabilitation in multiple sclerosis: a SWOT analysis and the synergies with virtual and augmented environments.Front Robot AI. 2024 Feb 27;11:1335147. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1335147. eCollection 2024. Front Robot AI. 2024. PMID: 38638271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posthoc Interpretability of Neural Responses by Grouping Subject Motor Imagery Skills Using CNN-Based Connectivity.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 2;23(5):2750. doi: 10.3390/s23052750. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904950 Free PMC article.
-
Paradigms and methods of noninvasive brain-computer interfaces in motor or communication assistance and rehabilitation: a systematic review.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025 Aug;63(8):2209-2233. doi: 10.1007/s11517-025-03340-y. Epub 2025 Mar 10. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2025. PMID: 40059266 Review.
-
EEG Amplitude Modulation Analysis across Mental Tasks: Towards Improved Active BCIs.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;23(23):9352. doi: 10.3390/s23239352. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067725 Free PMC article.
-
A Hybrid Stacked Restricted Boltzmann Machine with Sobel Directional Patterns for Melanoma Prediction in Colored Skin Images.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;13(6):1104. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13061104. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raggi A., Monasta L., Beghi E., Caso V., Castelpietra G., Mondello S., Giussani G., Logroscino G., Magnani F.G., Piccininni M., et al. Incidence, Prevalence and Disability Associated with Neurological Disorders in Italy between 1990 and 2019: An Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Neurol. 2022;269:2080–2098. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10774-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benjamin E.J., Muntner P., Alonso A., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Das S.R., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56–e528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hatem S.M., Saussez G., della Faille M., Prist V., Zhang X., Dispa D., Bleyenheuft Y. Rehabilitation of Motor Function after Stroke: A Multiple Systematic Review Focused on Techniques to Stimulate Upper Extremity Recovery. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016;10:442. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00442. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Y., Yang Z., Chen X., Yuan H., Liu W. A Stacking Model Using URL and HTML Features for Phishing Webpage Detection. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019;94:27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2018.11.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

