Development of a Single-Chain Variable Fragment of CR3022 for a Plasmonic-Based Biosensor Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
- PMID: 36551102
- PMCID: PMC9776105
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121133
Development of a Single-Chain Variable Fragment of CR3022 for a Plasmonic-Based Biosensor Targeting the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein
Abstract
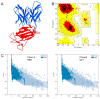
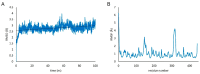
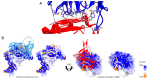
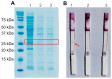
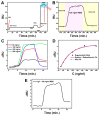
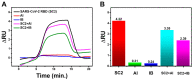
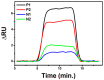
Two years after SARS-CoV-2 caused the first case of COVID-19, we are now in the "new normal" period, where people's activity has bounced back, followed by the easing of travel policy restrictions. The lesson learned is that the wide availability of accurate and rapid testing procedures is crucial to overcome possible outbreaks in the future. Therefore, many laboratories worldwide have been racing to develop a new point-of-care diagnostic test. To aid continuous innovation, we developed a plasmonic-based biosensor designed explicitly for portable Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR). In this study, we designed a single chain variable fragment (scFv) from the CR3022 antibody with a particular linker that inserted a cysteine residue at the second position. It caused the linker to have a strong affinity to the gold surface through thiol-coupling and possibly become a ready-to-use bioreceptor toward a portable SPR gold chip without purification steps. The theoretical affinity of this scFv on spike protein was -64.7 kcal/mol, computed using the Molecular Mechanics Generalized Born Surface Area (MM/GBSA) method from the 100 ns molecular dynamics trajectory. Furthermore, the scFv was produced in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) as a soluble protein. The binding activity toward Spike Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) SARS-CoV-2 was confirmed with a spot-test, and the experimental binding free energy of -10.82 kcal/mol was determined using portable SPR spectroscopy. We hope this study will be useful in designing specific and low-cost bioreceptors, particularly early in an outbreak when the information on antibody capture is still limited.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; molecular dynamics; plasmonic-based bioreceptor; portable SPR; scFv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

