Optical Light Sources and Wavelengths within the Visible and Near-Infrared Range Using Photoacoustic Effects for Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 36551121
- PMCID: PMC9775951
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121154
Optical Light Sources and Wavelengths within the Visible and Near-Infrared Range Using Photoacoustic Effects for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
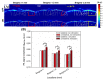
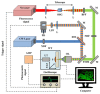
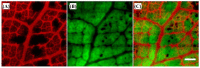
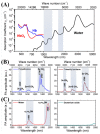
The photoacoustic (PA) effect occurs when sound waves are generated by light according to the thermodynamic and optical properties of the materials; they are absorption spectroscopic techniques that can be applied to characterize materials that absorb pulse or continuous wave (CW)-modulated electromagnetic radiation. In addition, the wavelengths and properties of the incident light significantly impact the signal-to-ratio and contrast with photoacoustic signals. In this paper, we reviewed how absorption spectroscopic research results have been used in applying actual photoacoustic effects, focusing on light sources of each wavelength. In addition, the characteristics and compositions of the light sources used for the applications were investigated and organized based on the absorption spectrum of the target materials. Therefore, we expect that this study will help researchers (who desire to study photoacoustic effects) to more efficiently approach the appropriate conditions or environments for selecting the target materials and light sources.
Keywords: optical source; photoacoustic effect; photoacoustic material; wavelength.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Hybrid multi-wavelength photoacoustic imaging.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018 Jul;2018:4804-4807. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8513153. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018. PMID: 30441421
-
Contrast Agents for Photoacoustic Imaging: A Review Focusing on the Wavelength Range.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 3;12(8):594. doi: 10.3390/bios12080594. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36004990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoacoustic detection and optical spectroscopy of high-intensity focused ultrasound-induced thermal lesions in biologic tissue.Med Phys. 2014 May;41(5):053502. doi: 10.1118/1.4871621. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24784408
-
Nonlinear Photoacoustic Imaging by in situ Multiphoton Upconversion and Energy Transfer.ACS Photonics. 2017 Nov 15;4(11):2699-2705. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00399. Epub 2017 Oct 11. ACS Photonics. 2017. PMID: 30246053 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Photoacoustic-Based Devices for Biomedical Applications.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 6;22(23):9541. doi: 10.3390/s22239541. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36502258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of Microcirculation at Acupoints in vivo of Alzheimer's Disease Animal Model with Photoacoustic Microscope: A Pilot Study.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024 Apr 8;8(1):561-574. doi: 10.3233/ADR-230193. eCollection 2024. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2024. PMID: 38746630 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Preamplifier for Ultrasound Transducers.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 25;24(3):786. doi: 10.3390/s24030786. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capped Plasmonic Gold and Silver Nanoparticles with Porphyrins for Potential Use as Anticancer Agents-A Review.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Sep 28;16(10):1268. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101268. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Inverse Class-E Power Amplifier for Ultrasound Transducer.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Mar 26;23(7):3466. doi: 10.3390/s23073466. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37050526 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time ancillary diagnostics for intraoperative assessment of intestinal viability in horses-looking for answers across species.Vet Surg. 2025 May;54(4):648-664. doi: 10.1111/vsu.14248. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Vet Surg. 2025. PMID: 40114354 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bell A.G. Upon the Production and Reproduction of Sound by Light. J. Soc. Telegr. Eng. 1880;9:404–426. doi: 10.1049/jste-1.1880.0046. - DOI
-
- Murray T.W., Balogun O. High-Sensitivity Laser-Based Acoustic Microscopy Using a Modulated Excitation Source. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004;85:2974–2976. doi: 10.1063/1.1802387. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

