Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection
- PMID: 36551132
- PMCID: PMC9775130
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121166
Triple Enhancement for Sensitive Immunochromatographic Assay: A Case Study for Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Detection
Abstract
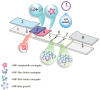
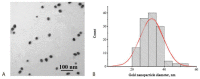
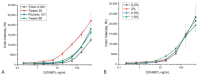
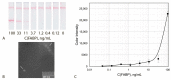
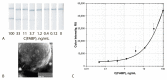
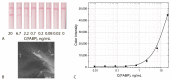
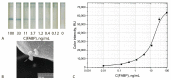
The work considers a combination of three enhancing approaches for immunochromatographic assay (ICA) and the integration of their impacts into changes of the limit of detection (LOD). Human fatty acid binding protein (FABP), an early biomarker of acute myocardial infarction, was the target analyte. Starting from the common ICA protocol with an LOD equal to 11.2 ng/mL, three approaches were realized: (1) replacement of spherical gold nanoparticles with gold nanoflowers having a branched surface (20-fold lowering the LOD); (2) enhanced labeling of immune complexes via nanoparticle aggregates (15-fold lowering); (3) in-situ growth of bound nanoparticles by reduction of gold salts (3-fold lowering). Single and combined implementations of these approaches have been studied. It has been shown that the LOD decrease for combined approaches is close to the multiplied contribution of each of them. The final LOD for FABP was 0.05 ng/mL, which is 220 times lower than the LOD for the common ICA protocol. The efficiency of the enhanced ICA with three combined approaches was confirmed by testing human serum samples for FABP presence and content. The development presents a new efficient technique for rapid sensitive detection of FABP for medical diagnostics. Moreover, the demonstrated multiple enhancements could be applied for various demanded analytes.
Keywords: cardiomarker; fatty acid binding protein; gold nanoparticles; immunochromatography; sensitivity enhancement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gold nanoparticle-decorated metal organic frameworks on immunochromatographic assay for human chorionic gonadotropin detection.Mikrochim Acta. 2020 Nov 5;187(12):640. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-04617-9. Mikrochim Acta. 2020. PMID: 33151410
-
Advantages of Highly Spherical Gold Nanoparticles as Labels for Lateral Flow Immunoassay.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jun 26;20(12):3608. doi: 10.3390/s20123608. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32604874 Free PMC article.
-
Developing an ultrasensitive immunochromatographic assay for authentication of an emergent fraud aminopyrine in herbal tea.Food Chem. 2023 Apr 16;406:135065. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135065. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36462351
-
Enhanced immunochromatographic assay using multifunctional gold@iridium nanoflower with colorimetric photothermal catalytic activity for the detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B.Food Chem. 2024 Dec 1;460(Pt 3):140710. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140710. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 39106748
-
Rapid and sensitive detection of tert-butylhydroquinone in soybean oil using a gold-based paper sensor.Analyst. 2022 May 3;147(9):1906-1914. doi: 10.1039/d2an00265e. Analyst. 2022. PMID: 35352722
References
-
- Xing K.-Y., Shan S., Liu D.-F., Lai W.-H. Recent advances of lateral flow immunoassay for mycotoxins detection. TrAC. 2020;133:116087. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2020.116087. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

