Optical Methods for Label-Free Detection of Bacteria
- PMID: 36551138
- PMCID: PMC9775963
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12121171
Optical Methods for Label-Free Detection of Bacteria
Abstract
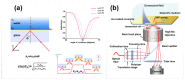
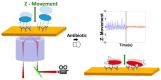
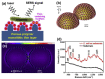
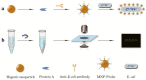
Pathogenic bacteria are the leading causes of food-borne and water-borne infections, and one of the most serious public threats. Traditional bacterial detection techniques, including plate culture, polymerase chain reaction, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay are time-consuming, while hindering precise therapy initiation. Thus, rapid detection of bacteria is of vital clinical importance in reducing the misuse of antibiotics. Among the most recently developed methods, the label-free optical approach is one of the most promising methods that is able to address this challenge due to its rapidity, simplicity, and relatively low-cost. This paper reviews optical methods such as surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy, surface plasmon resonance, and dark-field microscopic imaging techniques for the rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria in a label-free manner. The advantages and disadvantages of these label-free technologies for bacterial detection are summarized in order to promote their application for rapid bacterial detection in source-limited environments and for drug resistance assessments.
Keywords: Raman spectroscopy; bacteria detection; dark-field microscopy; label-free; rapid detection; surface plasmon resonance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent advances in rapid pathogen detection method based on biosensors.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Jun;37(6):1021-1037. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3230-x. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29569045 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Bacterial Detection Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Aug 1;14(8):375. doi: 10.3390/bios14080375. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid label-free identification of mixed bacterial infections by surface plasmon resonance.J Transl Med. 2011 Jun 7;9:85. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-85. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21649913 Free PMC article.
-
[Studies on rapid detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria by nucleic acid testing and related technology].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2008 Mar;37(2):245-8. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2008. PMID: 18589620 Review. Chinese.
-
Label and label-free based surface-enhanced Raman scattering for pathogen bacteria detection: A review.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Aug 15;94:131-140. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.02.032. Epub 2017 Feb 28. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 28262610 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid discrimination between wild and cultivated Ophiocordyceps sinensis through comparative analysis of label-free SERS technique and mass spectrometry.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Aug 14;9:100820. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100820. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39263205 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Methods for Routine Identification of Airborne Microorganisms in Speleotherapeutic Caves.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 14;12(7):1427. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071427. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065195 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating the Tiny World: A Navigation Guide for Proper Raman Studies on Microorganisms.Molecules. 2024 Feb 29;29(5):1077. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051077. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Optical Sensing for the Detection of Microbial Contaminants.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Aug 26;14(9):1668. doi: 10.3390/mi14091668. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lighting the Path: Raman Spectroscopy's Journey Through the Microbial Maze.Molecules. 2024 Dec 17;29(24):5956. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245956. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Havelaar A.H., Kirk M.D., Torgerson P.R., Gibb H.J., Hald T., Lake R.J., Praet N., Bellinger D.C., de Silva N.R., Gargouri N., et al. World Health Organization Global Estimates and Regional Comparisons of the Burden of Foodborne Disease in 2010. PLoS Med. 2015;12:e1001923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001923. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu X., Han C., Chen J., Huang Y.-W., Zhao Y. Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria from Fresh Produce by Filtration and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Miner. 2016;68:1156–1162. doi: 10.1007/s11837-015-1724-x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

