Regulation Mechanisms of Meiotic Recombination Revealed from the Analysis of a Fission Yeast Recombination Hotspot ade6-M26
- PMID: 36551189
- PMCID: PMC9775316
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12121761
Regulation Mechanisms of Meiotic Recombination Revealed from the Analysis of a Fission Yeast Recombination Hotspot ade6-M26
Abstract
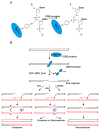
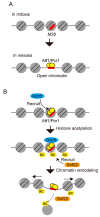
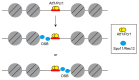
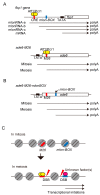
Meiotic recombination is a pivotal event that ensures faithful chromosome segregation and creates genetic diversity in gametes. Meiotic recombination is initiated by programmed double-strand breaks (DSBs), which are catalyzed by the conserved Spo11 protein. Spo11 is an enzyme with structural similarity to topoisomerase II and induces DSBs through the nucleophilic attack of the phosphodiester bond by the hydroxy group of its tyrosine (Tyr) catalytic residue. DSBs caused by Spo11 are repaired by homologous recombination using homologous chromosomes as donors, resulting in crossovers/chiasmata, which ensure physical contact between homologous chromosomes. Thus, the site of meiotic recombination is determined by the site of the induced DSB on the chromosome. Meiotic recombination is not uniformly induced, and sites showing high recombination rates are referred to as recombination hotspots. In fission yeast, ade6-M26, a nonsense point mutation of ade6 is a well-characterized meiotic recombination hotspot caused by the heptanucleotide sequence 5'-ATGACGT-3' at the M26 mutation point. In this review, we summarize the meiotic recombination mechanisms revealed by the analysis of the fission ade6-M26 gene as a model system.
Keywords: Rec12 (fission yeast Spo11 homolog); S. pombe; chromatin; double strand break (DSB); meiotic recombination; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Correlation of Meiotic DSB Formation and Transcription Initiation Around Fission Yeast Recombination Hotspots.Genetics. 2017 Jun;206(2):801-809. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.197954. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28396503 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple modes of chromatin configuration at natural meiotic recombination hot spots in fission yeast.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Nov;6(11):2072-80. doi: 10.1128/EC.00246-07. Epub 2007 Sep 7. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17827346 Free PMC article.
-
Active and inactive transplacement of the M26 recombination hotspot in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Genetics. 1995 Sep;141(1):33-48. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.1.33. Genetics. 1995. PMID: 8536980 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved histone variant H2A.Z illuminates meiotic recombination initiation.Curr Genet. 2018 Oct;64(5):1015-1019. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0825-9. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29549582 Review.
-
The meiotic recombination hotspots of Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Genome Dyn. 2009;5:1-13. doi: 10.1159/000166614. Genome Dyn. 2009. PMID: 18948703 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic stress-induced long ncRNA transcription governs the formation of meiotic DNA breaks in the fission yeast fbp1 gene.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 22;19(1):e0294191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294191. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38252660 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

