SNARE Modulators and SNARE Mimetic Peptides
- PMID: 36551207
- PMCID: PMC9776023
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12121779
SNARE Modulators and SNARE Mimetic Peptides
Abstract
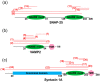
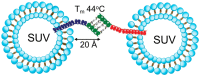
The soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF) attachment protein (SNAP) receptor (SNARE) proteins play a central role in most forms of intracellular membrane trafficking, a key process that allows for membrane and biocargo shuffling between multiple compartments within the cell and extracellular environment. The structural organization of SNARE proteins is relatively simple, with several intrinsically disordered and folded elements (e.g., SNARE motif, N-terminal domain, transmembrane region) that interact with other SNAREs, SNARE-regulating proteins and biological membranes. In this review, we discuss recent advances in the development of functional peptides that can modify SNARE-binding interfaces and modulate SNARE function. The ability of the relatively short SNARE motif to assemble spontaneously into stable coiled coil tetrahelical bundles has inspired the development of reduced SNARE-mimetic systems that use peptides for biological membrane fusion and for making large supramolecular protein complexes. We evaluate two such systems, based on peptide-nucleic acids (PNAs) and coiled coil peptides. We also review how the self-assembly of SNARE motifs can be exploited to drive on-demand assembly of complex re-engineered polypeptides.
Keywords: SNARE mimetic; SNARE motif; SNARE peptide; SNARE protein; SNAREpins; clostridial neurotoxins; functional peptide; fusogen; membrane fusion; molecular self-assembly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
α-SNAP Enhances SNARE Zippering by Stabilizing the SNARE Four-Helix Bundle.Cell Rep. 2016 Apr 19;15(3):531-539. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.03.050. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27068468 Free PMC article.
-
A novel site of action for alpha-SNAP in the SNARE conformational cycle controlling membrane fusion.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Mar;19(3):776-84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-05-0498. Epub 2007 Dec 19. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18094056 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved membrane attachment site in alpha-SNAP facilitates N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor (NSF)-driven SNARE complex disassembly.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):31817-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.045286. Epub 2009 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19762473 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular functions of NSF: not just SNAPs and SNAREs.FEBS Lett. 2007 May 22;581(11):2140-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.03.032. Epub 2007 Mar 21. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17397838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane fusion: SNAREs and regulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Sep;65(18):2814-32. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8352-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18726177 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resequencing of the TMF-1 (TATA Element Modulatory Factor) regulated protein (TRNP1) gene in domestic and wild canids.Canine Med Genet. 2023 Nov 15;10(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40575-023-00133-0. Canine Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37968761 Free PMC article.
-
Trypsin in pancreatitis: The culprit, a mediator, or epiphenomenon?World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Nov 7;30(41):4417-4438. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i41.4417. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39534420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Conformational Space of the Translocation Domain of Botulinum Toxin: Atomistic Modeling and Mesoscopic Description of the Coiled-Coil Helix Bundle.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 20;25(5):2481. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052481. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473729 Free PMC article.
-
SNAP25 is a potential target for early stage Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Dec 6;28(1):570. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01360-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38053192 Free PMC article.
-
Protein structure-function continuum model: Emerging nexuses between specificity, evolution, and structure.Protein Sci. 2024 Apr;33(4):e4968. doi: 10.1002/pro.4968. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38532700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

