Eosinophils Infiltration in Esophageal Muscularis Propria Induces Achalasia-like Esophageal Motility Disorder in Mice
- PMID: 36551293
- PMCID: PMC9775547
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12121865
Eosinophils Infiltration in Esophageal Muscularis Propria Induces Achalasia-like Esophageal Motility Disorder in Mice
Abstract
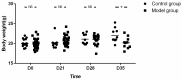
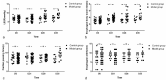
Eosinophil infiltration in esophageal muscularis propria is common in achalasia (AC). This study aims to evaluate the effect of eosinophil infiltration in muscularis propria of the esophagus on esophageal motility in mice. A mouse model with eosinophil infiltration in the esophageal muscle layer was established by long term Ovalbumin (OVA) exposure. The histopathology features of esophageal muscularis propria as well as parameters of esophageal motility, such as lower esophageal sphincter pressure (LESP) and esophageal emptying, were compared between model and control group. In addition, the histopathology and motility of esophagus at each time point in the model group were compared. The esophageal motor function severely deteriorated in the model group, mimicking the abnormal esophageal motility of AC, with more eosinophils and fewer SOX-10-IR cells in esophageal muscularis propria in the model group, compared with control. With the prolongation of OVA treatment, esophageal motility disorder was aggravated, accompanied by increased eosinophils in the the muscle layer of esophagus and decreased SOX-10-IR cells in the model group. In addition, the eosinophil count was negatively correlated with SOX-10-IR cells. Long-term exposure to OVA assisted by alum may induce eosinophil infiltration in esophageal muscularis propria, reduced SOX-10-IR cells and abnormal esophageal motility, which simulates the functional and histopathological features of some AC patients. This suggests that eosinophil infiltration in esophageal muscularis propria may play a role in the pathogenesis of a subgroup of AC.
Keywords: achalasia; eosinophil; mice.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Can Eosinophilic Esophagitis Cause Achalasia and Other Esophageal Motility Disorders?Am J Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov;113(11):1594-1599. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0240-3. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30315308 Review.
-
Pattern of esophageal eosinophilic infiltration in patients with achalasia and response to Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication.Dis Esophagus. 2013 Nov-Dec;26(8):766-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2012.01385.x. Epub 2012 Aug 14. Dis Esophagus. 2013. PMID: 22891632
-
Muscle layer histopathology and manometry pattern of primary esophageal motility disorders including achalasia.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017 Mar;29(3). doi: 10.1111/nmo.12968. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2017. PMID: 27699951
-
Mast cell effects on esophageal smooth muscle and their potential role in eosinophilic esophagitis and achalasia.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Mar 1;320(3):G319-G327. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00290.2020. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33355505 Review.
-
Simultaneous Examination of Eosinophil Infiltration in Esophageal Mucosa and Muscle in Patients with Achalasia: Direct Biopsy of the Esophageal Muscle at Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 Jan;67(1):170-176. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06827-4. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 33502676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Z.-Q., Chen W.-F., Wang Y., Xu X.-Y., Zeng Y.-G., Dillon D.L., Cheng J., Xu M.-D., Zhong Y.-S., Zhang Y.-Q., et al. Mast cell infiltration associated with loss of interstitial cells of Cajal and neuronal degeneration in achalasia. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019;31:e13565. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13565. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

