PurN Is Involved in Antibiotic Tolerance and Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 36551359
- PMCID: PMC9774800
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11121702
PurN Is Involved in Antibiotic Tolerance and Virulence in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
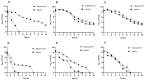
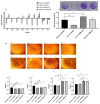
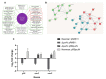
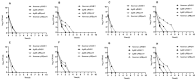
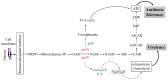
Staphylococcus aureus can cause chronic infections which are closely related to persister formation. Purine metabolism is involved in S. aureus persister formation, and purN, encoding phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase, is an important gene in the purine metabolism process. In this study, we generated a ΔpurN mutant of the S. aureus Newman strain and assessed its roles in antibiotic tolerance and virulence. The ΔpurN in the late exponential phase had a significant defect in persistence to antibiotics. Complementation of the ΔpurN restored its tolerance to different antibiotics. PurN significantly affected virulence gene expression, hemolytic ability, and biofilm formation in S. aureus. Moreover, the LD50 (3.28 × 1010 CFU/mL) of the ΔpurN for BALB/c mice was significantly higher than that of the parental strain (2.81 × 109 CFU/mL). Transcriptome analysis revealed that 58 genes that were involved in purine metabolism, alanine, aspartate, glutamate metabolism, and 2-oxocarboxylic acid metabolism, etc., were downregulated, while 24 genes involved in ABC transporter and transferase activity were upregulated in ΔpurN vs. parental strain. Protein-protein interaction network showed that there was a close relationship between PurN and GltB, and SaeRS. The study demonstrated that PurN participates in the formation of the late exponential phase S. aureus persisters via GltB and regulates its virulence by activating the SaeRS two-component system.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; persister; purN; purine metabolism; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
gltB encoding glutamate synthase is involved in persister and biofilm formation and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Aug 12:e0051125. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00511-25. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40793764
-
The impact of inactivation of the purine biosynthesis genes, purN and purT, on growth and virulence in uropathogenic E. coli.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):2707-2716. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4441-z. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30377949
-
Genetic Screen Reveals the Role of Purine Metabolism in Staphylococcus aureus Persistence to Rifampicin.Antibiotics (Basel). 2015 Dec 7;4(4):627-42. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics4040627. Antibiotics (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27025643 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus chronic and relapsing infections: Evidence of a role for persister cells: An investigation of persister cells, their formation and their role in S. aureus disease.Bioessays. 2014 Oct;36(10):991-6. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400080. Epub 2014 Aug 6. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 25100240 Review.
-
Staphylococcus aureus Small Colony Variants (SCVs): a road map for the metabolic pathways involved in persistent infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Jul 28;4:99. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00099. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25120957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative analysis of genes expression involved in type II toxin-antitoxin system in Staphylococcus aureus following persister cell formation.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 23;51(1):324. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09179-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38393536
-
Bacterial persisters: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic development.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Jul 17;9(1):174. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01866-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39013893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Master Switch: Pyruvate Carboxylase Fuels Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence in Foodborne Staphylococcus aureus.Foods. 2025 Jul 22;14(15):2566. doi: 10.3390/foods14152566. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807502 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced immunity: the gut microbiota changes in high-altitude Tibetan pigs compared to Yorkshire pigs.Front Microbiol. 2024 Nov 18;15:1469253. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1469253. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39624721 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and Proteomic Dissection of the Contributions of CodY, SigB and the Hibernation Promoting Factor HPF to Interactions of Staphylococcus aureus USA300 with Human Lung Epithelial Cells.J Proteome Res. 2024 Oct 4;23(10):4742-4760. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00724. Epub 2024 Sep 20. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 39302699 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dayan G.H., Mohamed N., Scully I.L., Cooper D., Begier E., Eiden J., Jansen K.U., Gurtman A., Anderson A.S. Staphylococcus aureus: The current state of disease, pathophysiology and strategies for prevention. Expert. Rev. Vaccines. 2016;15:1373–1392. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2016.1179583. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

