Protective Effects of Combined Utilization of Quercetin and Florfenicol on Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Syndrome Infected Litopenaeus vannamei
- PMID: 36551441
- PMCID: PMC9774288
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11121784
Protective Effects of Combined Utilization of Quercetin and Florfenicol on Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Syndrome Infected Litopenaeus vannamei
Abstract
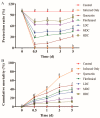
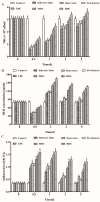
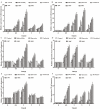
This study aimed to determine the immunity, survival rate, and disease resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei treated using quercetin and florfenicol alone or in combination, after infection with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus (VPAHPND). After infection with VPAHPND, different types of feed were given to the shrimp for 5 days, including a control diet (drug-free), florfenicol only diet (15 mg/kg), quercetin only diet (400 mg/kg), a low-dose florfenicol/quercetin combined diet (200 mg/kg quercetin + 7.0 mg/kg florfenicol), a moderate-dose florfenicol/quercetin combined diet (400 mg/kg quercetin + 15 mg/kg florfenicol), and a high-dose florfenicol/quercetin combined diet (800 mg/kg quercetin + 30 mg/kg florfenicol). The cumulative mortality of shrimp was significantly reduced in the drug combination groups compared with either drug used alone (p < 0.05). The density of Vibrio was significantly lower and the immune parameters were significantly increased in the drug combination groups compared with either drug used alone (p < 0.05). Moreover, in the drug combination groups, the hepatopancreas tubules showed better integrity and structure compared with those when either drug was used alone. Therefore, compared with single drug treatment, the florfenicol and quercetin combination enhanced disease resistance, survival, and immune activity of VPAHPND-infected shrimp. When the combination treatment is used, the dosage of florfenicol can be reduced and a better therapeutic effect is obtained.
Keywords: Litopenaeus vannamei; VPAHPND; florfenicol; immunomodulation; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of combination effects of Astragalus polysaccharides and florfenicol against acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease-causing strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Litopenaeus vannamei.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Mar;86:374-383. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.11.065. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30502463
-
Effectiveness of traditional Chinese herbal medicine, San-Huang-San, in combination with enrofloxacin to treat AHPND-causing strain of Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in Litopenaeus vannamei.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Apr;87:360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Jan 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30630050
-
The immunomodulation of outer membrane vesicles from Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025 Jun;161:110274. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2025.110274. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40081434
-
In silico identification and functional study of long non-coding RNA involved in acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Sep;152:109768. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109768. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39013534
-
Integrated application of transcriptomics and metabolomics provides insights into acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease resistance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.mSystems. 2023 Aug 31;8(4):e0006723. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00067-23. Epub 2023 Jun 26. mSystems. 2023. PMID: 37358285 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the Potential: Quercetin and Its Natural Derivatives as Promising Therapeutics for Sepsis.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 16;12(2):444. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020444. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- MOA (Fisheries Bureau, Ministry of Agriculture) China Fishery Statistics Yearbook 2021. China Agriculture Press; Beijing, China: 2021. pp. 21–36.
-
- Rico A., Phu T.M., Satapornvanit K., Min J., Shahabuddin A.M., Henriksson P.J.G., Murray F.J., Little D.C., Dalsgaard A., Van den Brink P.J. Use of veterinary medicines, feed additives and probiotics in four major internationally traded aquaculture species farmed in Asia. Aquaculture. 2013;412–413:231–243. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.07.028. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 32102845/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019YFD0900403/National Key R&D Program of China
- ZR2019QC015/Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, P. R. China
- CARS-48/China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
- 2020TD46/Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

