Antimicrobial Efficacy against Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus Depends on the Mechanism of Antibiotic Tolerance
- PMID: 36551467
- PMCID: PMC9774428
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11121810
Antimicrobial Efficacy against Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus Depends on the Mechanism of Antibiotic Tolerance
Abstract
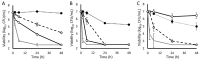
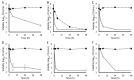
Bacteria can adapt to a changing environment by adopting alternate metabolic states favoring small molecule synthesis and resilience over growth. In Staphylococcus aureus, these states are induced by factors present during infection, including nutritional limitations, host responses and competition with other bacteria. Isogenic "tolerant" populations have variable responses to antibiotics and can remain viable. In this study, we compared the capability of antibiotics to reduce the viability of S. aureus made tolerant by different mechanisms. Tolerance was induced with mupirocin, HQNO, peroxynitrite or human serum. Tolerant cultures were exposed to ceftaroline, daptomycin, gentamicin, levofloxacin, oritavancin or vancomycin at physiological concentrations, and the viability was assessed by dilution plating. The minimum duration for 3-log viability reduction and 24 h viability reduction were calculated independently for each of three biological replicates. Each tolerance mechanism rendered at least one antibiotic ineffective, and each antibiotic was rendered ineffective by at least one mechanism of tolerance. Further studies to evaluate additional antibiotics, combination therapy and different tolerance inducers are warranted.
Keywords: MRSA; Staphylococcus aureus; persistence; tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct Effectiveness of Oritavancin against Tolerance-Induced Staphylococcus aureus.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Nov 8;9(11):789. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9110789. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33171631 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Daptomycin Tolerance and Resistance Mutations in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Adaptive Laboratory Evolution.mSphere. 2021 Oct 27;6(5):e0069221. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00692-21. Epub 2021 Sep 29. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34585959 Free PMC article.
-
The Neutrally Charged Diarylurea Compound PQ401 Kills Antibiotic-Resistant and Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2020 Jun 30;11(3):e01140-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01140-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32605985 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Outcomes of Ceftaroline plus Vancomycin or Daptomycin Combination Therapy versus Vancomycin or Daptomycin Monotherapy in Adults with Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia-A Meta-Analysis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 15;11(8):1104. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081104. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Treatment Options for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Bacteremia: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Nov 14;14(11):e31486. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31486. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36523711 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic tolerance among clinical isolates: mechanisms, detection, prevalence, and significance.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Dec 10;37(4):e0010624. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00106-24. Epub 2024 Oct 4. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39364999 Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides and Small Molecules Targeting the Cell Membrane of Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023 Jun 28;87(2):e0003722. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00037-22. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37129495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Complex Intracellular Lifecycle of Staphylococcus aureus Contributes to Reduced Antibiotic Efficacy and Persistent Bacteremia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 12;25(12):6486. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126486. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restriction of arginine induces antibiotic tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 7;15(1):6734. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51144-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39112491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kourtis A.P., Hatfield K., Baggs J., Mu Y., See I., Epson E., Nadle J., Kainer M.A., Dumyati G., Petit S., et al. Vital Signs: Epidemiology and Recent Trends in Methicillin-Resistant and in Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus Bloodstream Infections—United States. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019;68:214–219. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6809e1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

