Studies Regarding the Antimicrobial Behavior of Clotrimazole and Limonene
- PMID: 36551473
- PMCID: PMC9774930
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11121816
Studies Regarding the Antimicrobial Behavior of Clotrimazole and Limonene
Abstract
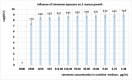
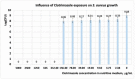
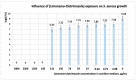
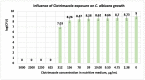
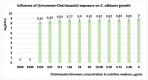
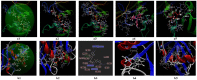
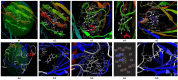
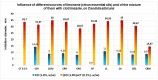
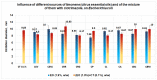
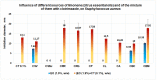
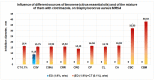
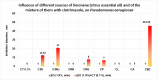
The paper presents the results of the studies performed to establish the effect of the mixtures between limonene and clotrimazole against microbial pathogens involved in dermatological diseases, such as Candida albicans, Staphyloccocus aureus, and Escherichia coli. Preliminary data obtained from the studies performed in microplates revealed a possible synergism between the mixture of clotrimazole and limonene for Staphylococcus aureus. Studies performed "in silico" with programs such as CLC Drug Discovery Workbench and MOLEGRO Virtual Docker, gave favorable scores for docking each compound on a specific binding site for each microorganism. The tests performed for validation, with the clotrimazole (0.1%) and different sources of limonene (1.9% citrus essential oils), showed a synergistic effect on Staphylococcus aureus in the case of the mixtures between clotrimazole and the essential oils of Citrus reticulata or Citrus paradisi. The studies performed on Staphylococcus aureus MRSA showed a synergistic effect between clotrimazole and the essential oils obtained from Citrus bergamia, Citrus aurantium, or Citrus paradisi. In the case of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, essential oils and clotrimazole used alone did not exhibit antimicrobial activities, but the mixtures between clotrimazole and the essential oils of Citrus bergamia or Citrus sinensis exhibited a synergistic antimicrobial effect.
Keywords: clotrimazole; limonene; synergistic effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Khan U.M., Sameen A., Aadil R.M., Shahid M., Sezen S., Zarrabi A., Ozdemir B., Sevindik M., Kaplan D.N., Selamoglu Z., et al. Citrus Genus and Its Waste Utilization: A Review on Health-Promoting Activities and Industrial Application. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021;2021:2488804. doi: 10.1155/2021/2488804. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suri S., Singh A., Nema P.K. Current applications of citrus fruit processing waste: A scientific outlook. Appl. Food Res. 2022;2:100050. doi: 10.1016/j.afres.2022.100050. - DOI
-
- Nogueira J.O.E., Campolina G.A., Batista L.R., Alves E., Caetano A.R.S., Brandão R.M., David Lee Nelson D.L., das Graças Cardoso M. Mechanism of action of various terpenes and phenylpropanoids against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021;368:fnab052. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnab052. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mohammed S.O.M., Babeanu N., Cornea C.P., Radu N. Limonene—A biomolecule with potential applications in regenerative medicine. Sci. Bulletin. Ser. F Biotechnol. 2022;26:139–148.
-
- Roman V., Radu N., Bostan M., Popa O., Tanasescu A.H. Effect of melaleuca alternifolia bioproduct on acute monocytic leukemia cells line. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2019;695:29–36. doi: 10.1080/15421406.2020.1723903. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

